Hey everyone! I'm Necati, part of the team behind VoltAgent. You might know us from our previous work on Refine, an open-source React framework. Building Refine taught us a lot about developer tools and the power of community.
Now, we've ventured into the exciting world of AI with VoltAgent.
I wanted to share a bit about our journey the challenges we faced trying to build AI agent applications, the frameworks we explored, and why we ultimately decided to create our own solution, VoltAgent.
How It All Started: The Early Hurdles of Building AI Apps
We pictured building our own chatbots, smart assistants, or agents that could automate complex tasks. But when we actually started coding, we quickly realized that working directly with the basic AI SDKs (from OpenAI, Google, etc.) meant writing a ton of boilerplate code, especially for anything beyond the absolute basics.
Things like managing state, connecting tools, talking to LLMs, and handling memory were problems we had to solve again and again for each new project. It felt repetitive, and honestly, a bit frustrating. Having built Refine, we knew we didn't want other developers to get bogged down by these same fundamental issues over and over.
Searching for Frameworks: Exploring What's Out There
To escape the boilerplate trap, we started looking into existing AI agent frameworks. There are some really cool projects out there, each tackling AI agent development from a different angle.
- Agno: An open-source platform designed to build, ship, and monitor agentic systems. We looked into its approach to being model-agnostic and providing agents with memory, knowledge, and tools, along with its built-in monitoring capabilities.
- CrewAI: A popular choice in Python for building multi-agent systems. We liked the idea of agents collaborating on tasks, defined by roles.
- AWS Multi-Agent Orchestrator: A powerful option if you're deep in the AWS ecosystem, designed for managing multiple agents within their services.
- Mastra: An open-source platform focused on agent-based workflow automation, where agents perform specific tasks and combine results.
- kaiban.js: A developer-friendly library in the TypeScript/JavaScript world, focusing on things like state management and streaming for LLMs. Its flexibility was appealing.
All these frameworks helped in certain ways. Some were great for multi-agent setups, others specialized in specific areas, and some focused heavily on the developer experience.
But we felt something crucial was still missing.
The "Black Box" Problem & Our Need for Observability
Our biggest frustration while using these frameworks was the "black box" problem. It was really hard to understand why our agents made certain decisions, what steps they took, which tools they used and when, or exactly what went wrong when an error occurred.
Looking at logs helped a bit, but it wasn't enough, especially as the agent interactions got more complex. We desperately needed a way to visualize and easily track what was going on inside the agent its "thought process" and interactions.
This is where we got inspired by n8n, the no-code/low-code automation tool. We loved n8n's canvas-based interface for visualizing and debugging workflows step-by-step. We thought, "Why can't we have something similar for AI agents?"
The Birth of VoltAgent: Focusing on Observability
Fueled by these experiences and needs, VoltAgent was born. Our goal was to provide the structure and convenience of a framework while tackling the AI "black box" problem head-on. When designing VoltAgent, our top priority became observability.
The key differentiator for VoltAgent is our VoltOps LLM Observability Platform. This console lets you visualize the entire lifecycle of your agents LLM interactions, tool usage, state changes, even their internal reasoning on an n8n-style canvas.
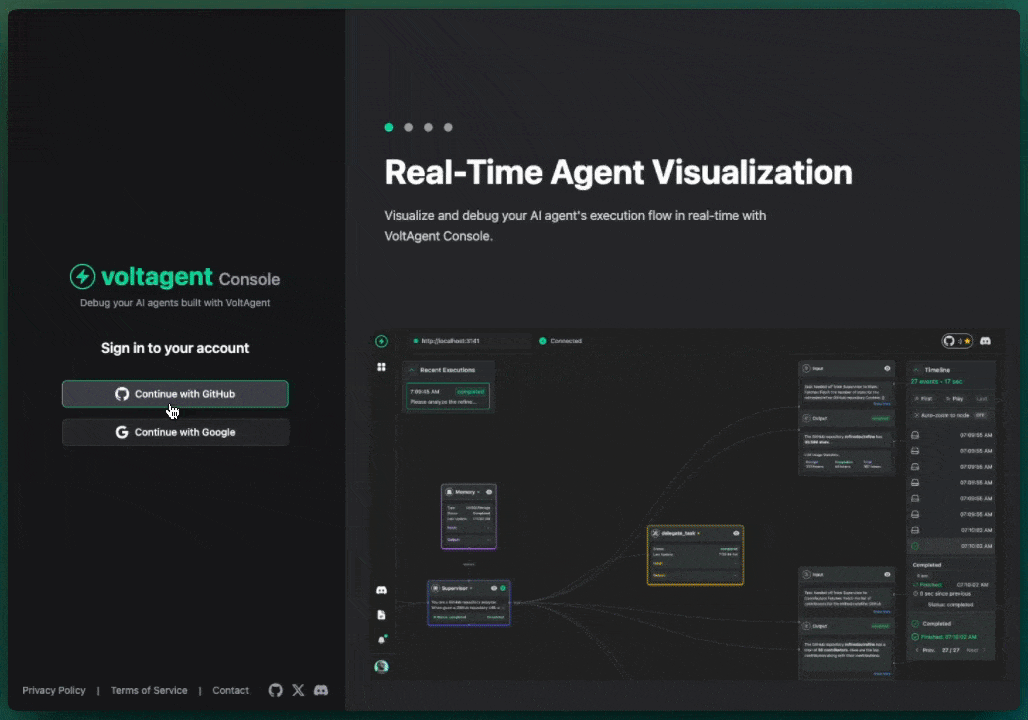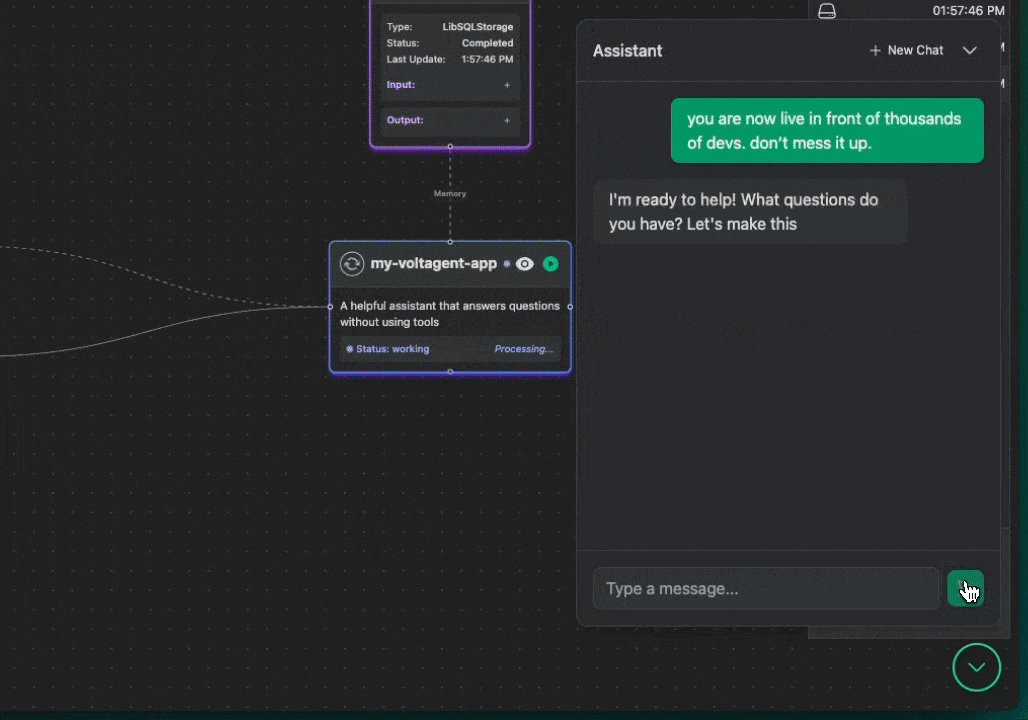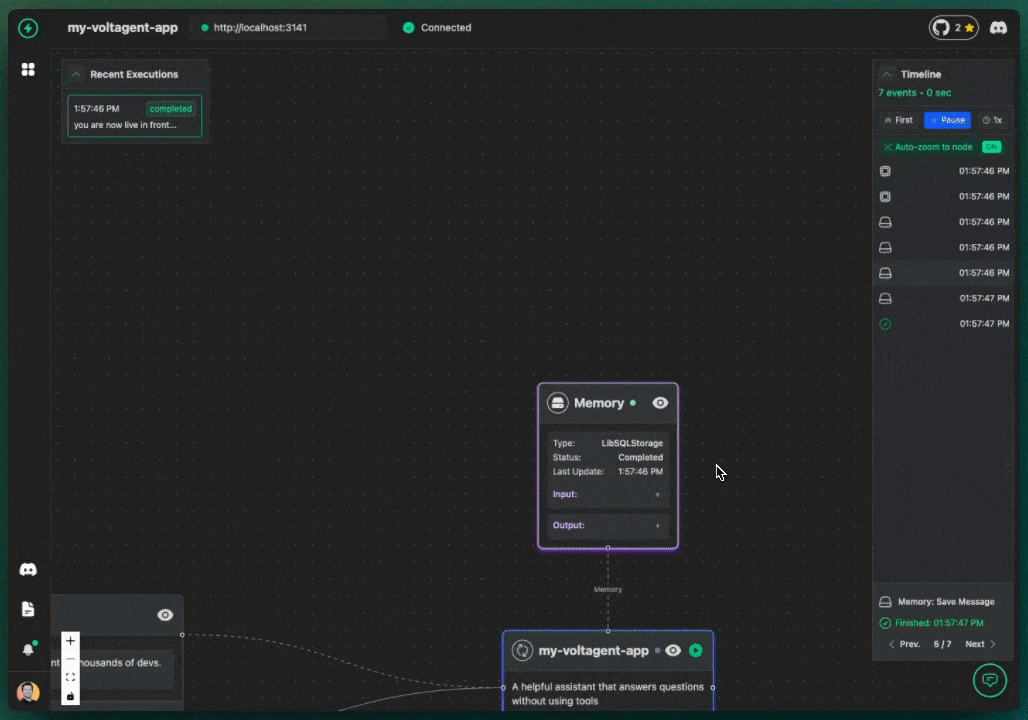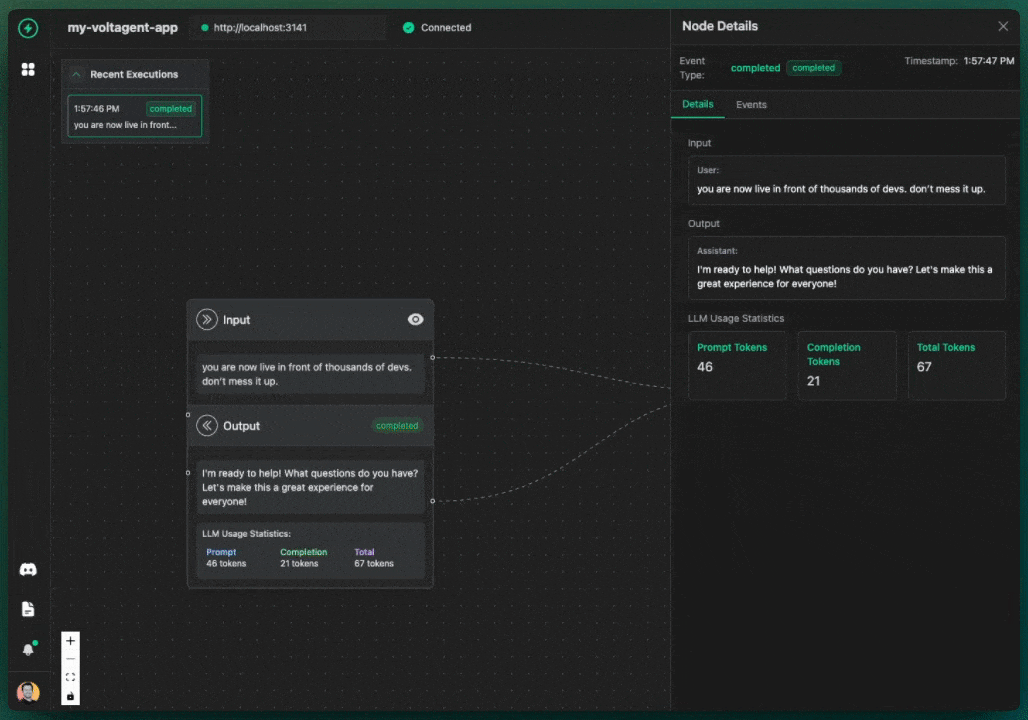
With this, you can:
- Clearly see the steps your agent takes to complete a task.
- Debug errors much more easily by pinpointing exactly where things went wrong.
- Track your agent's performance and LLM costs in detail.
- Easily compare results when experimenting with different LLMs or prompts.
While VoltAgent Core (@voltagent/core) gives you a flexible and powerful foundation, the VoltOps LLM Observability Platform makes the agents you build on top transparent and understandable.
Thanks and Looking ahead
We want to give a huge thank you to all the frameworks that inspired us along the way Agno, CrewAI, AWS, Mastra, kaiban.js, and tools like n8n.💫
Each one has made significant contributions to the growing AI agent ecosystem. It's this collective effort in the open-source community that allows all of us to build better tools together.
With VoltAgent, we aim to contribute back by focusing specifically on observability and the developer experience. We truly believe that understanding how agents work internally is key to creating more reliable, efficient, and powerful AI applications.
By the way, two major new features in the VoltAgent ecosystem will be announced soon.🤘
If you're building AI agents or just curious about the space, we'd love for you to give VoltAgent a try and share your feedback with us!