JavaScript/TypeScript SDK
Track your AI agents with full observability - traces, sub-agents, tools, memory operations, and more.
Installation
- npm
- pnpm
- Yarn
npm install @voltagent/sdk
pnpm add @voltagent/sdk
yarn add @voltagent/sdk
Setup
Initialize the SDK with your credentials:
import { VoltAgentObservabilitySDK } from "@voltagent/sdk";
const sdk = new VoltAgentObservabilitySDK({
baseUrl: "https://api.voltagent.dev",
publicKey: "your-public-key",
secretKey: "your-secret-key",
autoFlush: true, // Auto-send events
flushInterval: 3000, // Send every 3 seconds
});
Before using the SDK, you need to create an account at https://console.voltagent.dev/ and set up an organization and project to get your API keys.
Step-by-Step Guide
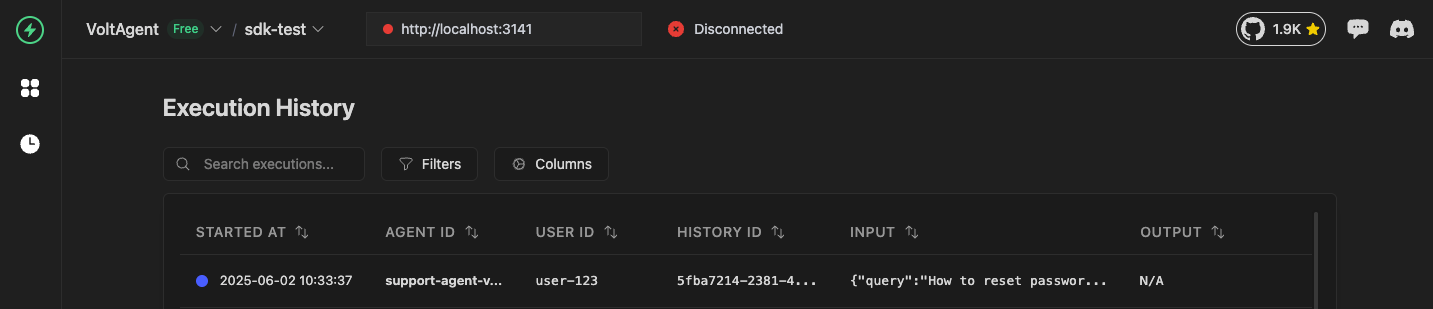
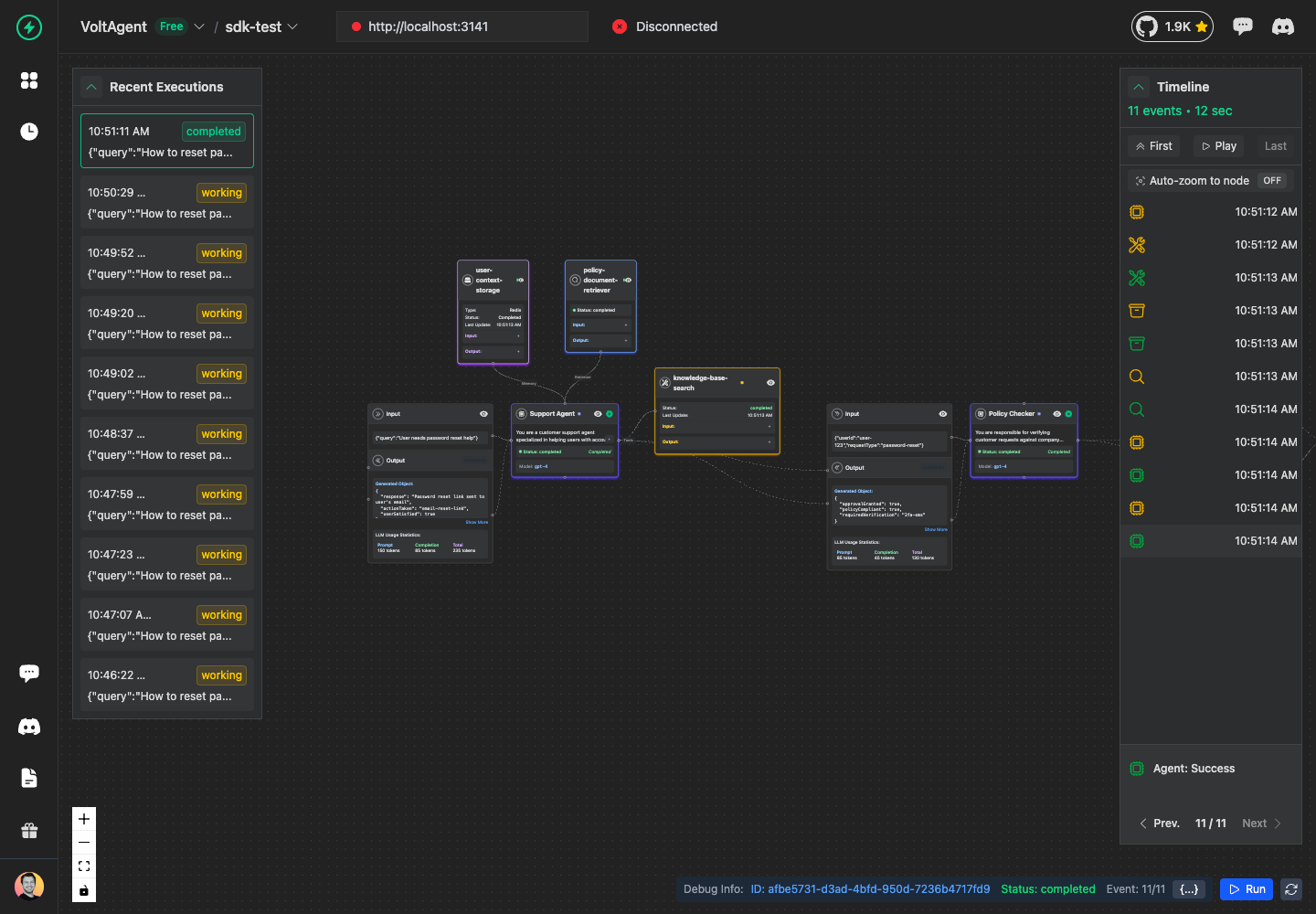
Create a Trace
A trace represents one complete agent execution session. Every agent operation must happen within a trace.
const trace = await sdk.trace({
name: "Customer Support Query",
agentId: "support-agent-v1",
input: { query: "How to reset password?" },
userId: "user-123",
conversationId: "conv-456",
tags: ["support", "password-reset"],
metadata: {
priority: "high",
source: "web-chat",
},
});
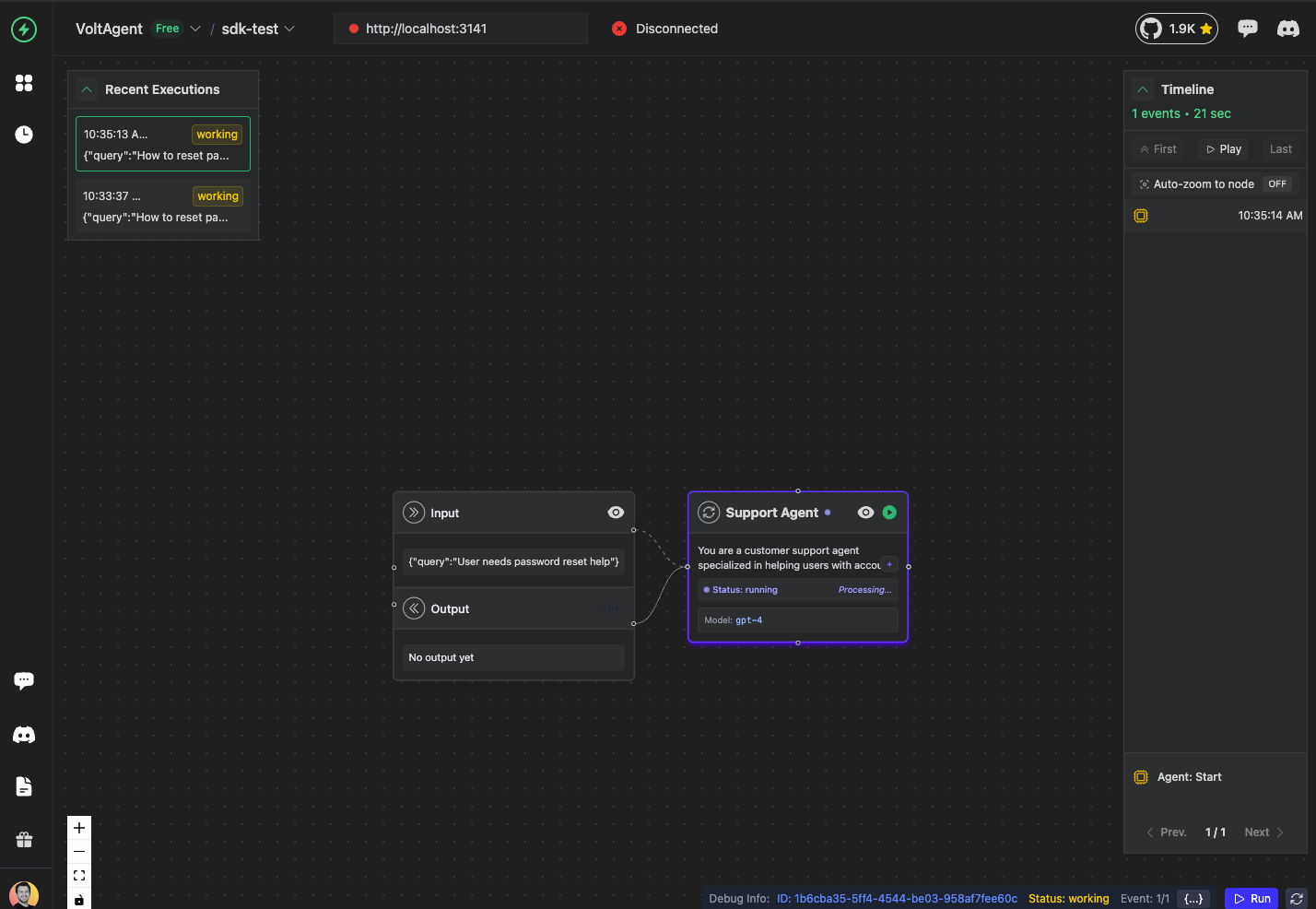
Add an Agent to the Trace
Now let's add the main agent that will handle the user's request:
const agent = await trace.addAgent({
name: "Support Agent",
input: { query: "User needs password reset help" },
instructions:
"You are a customer support agent specialized in helping users with account issues and password resets.",
metadata: {
modelParameters: {
model: "gpt-4",
},
},
});
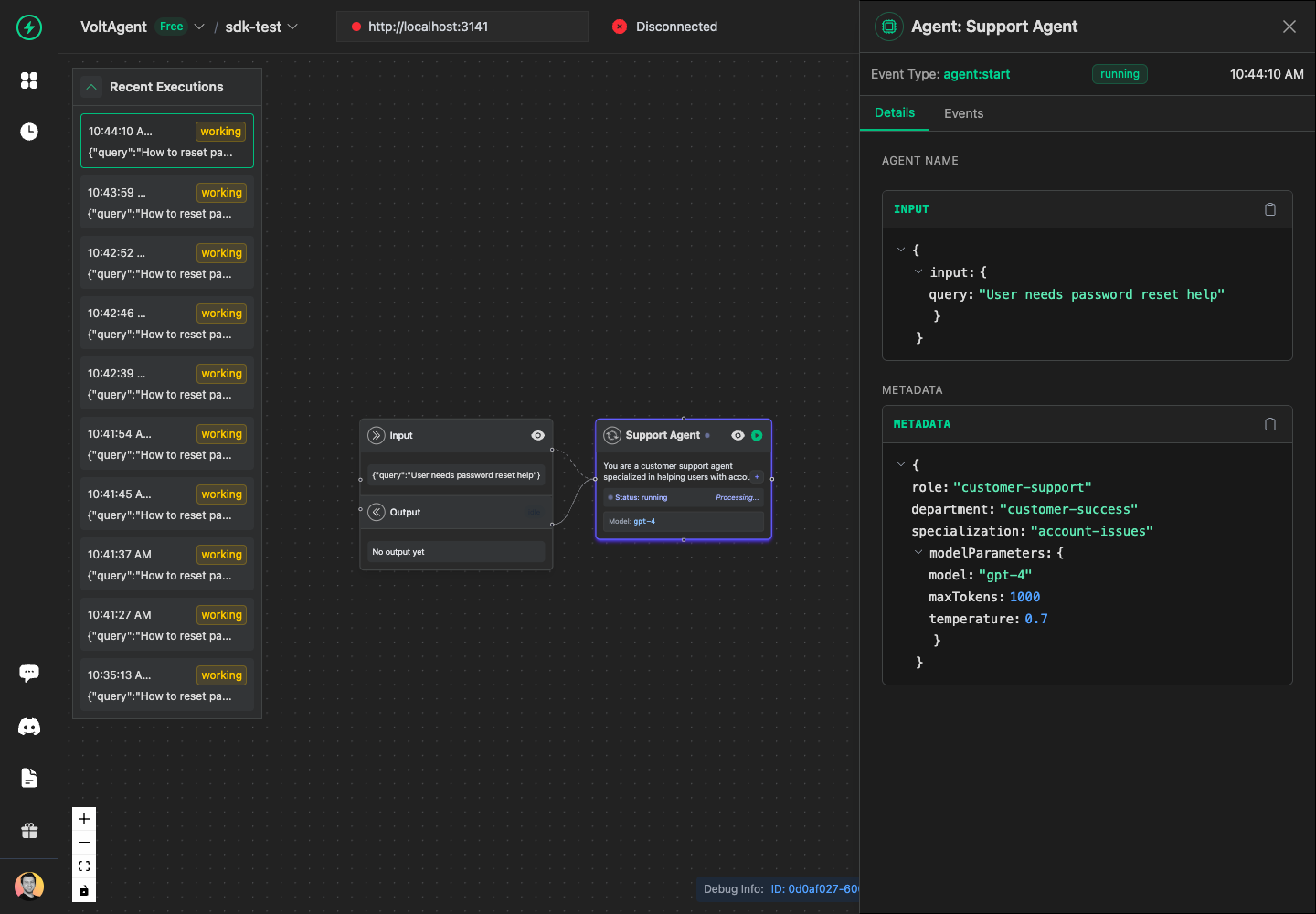
Understanding Agent Metadata
Agent metadata helps you organize and filter your observability data. Here's what each field means:
modelParameters: Model configuration including the AI model being used- Custom fields: Add any domain-specific metadata for your use case
metadata: {
modelParameters: {
model: "gpt-4",
temperature: 0.7,
maxTokens: 1000,
},
// Add your own custom metadata
role: "customer-support",
specialization: "account-issues",
department: "customer-success",
}
💡 Trace Completion
Traces can be completed in two ways:
Success:
await trace.end({
output: { result: "Query resolved successfully" },
status: "completed",
usage: { promptTokens: 150, completionTokens: 85, totalTokens: 235 },
});Error:
await trace.end({
output: { error: "Failed to process query" },
status: "error",
metadata: { errorCode: "TIMEOUT" },
});
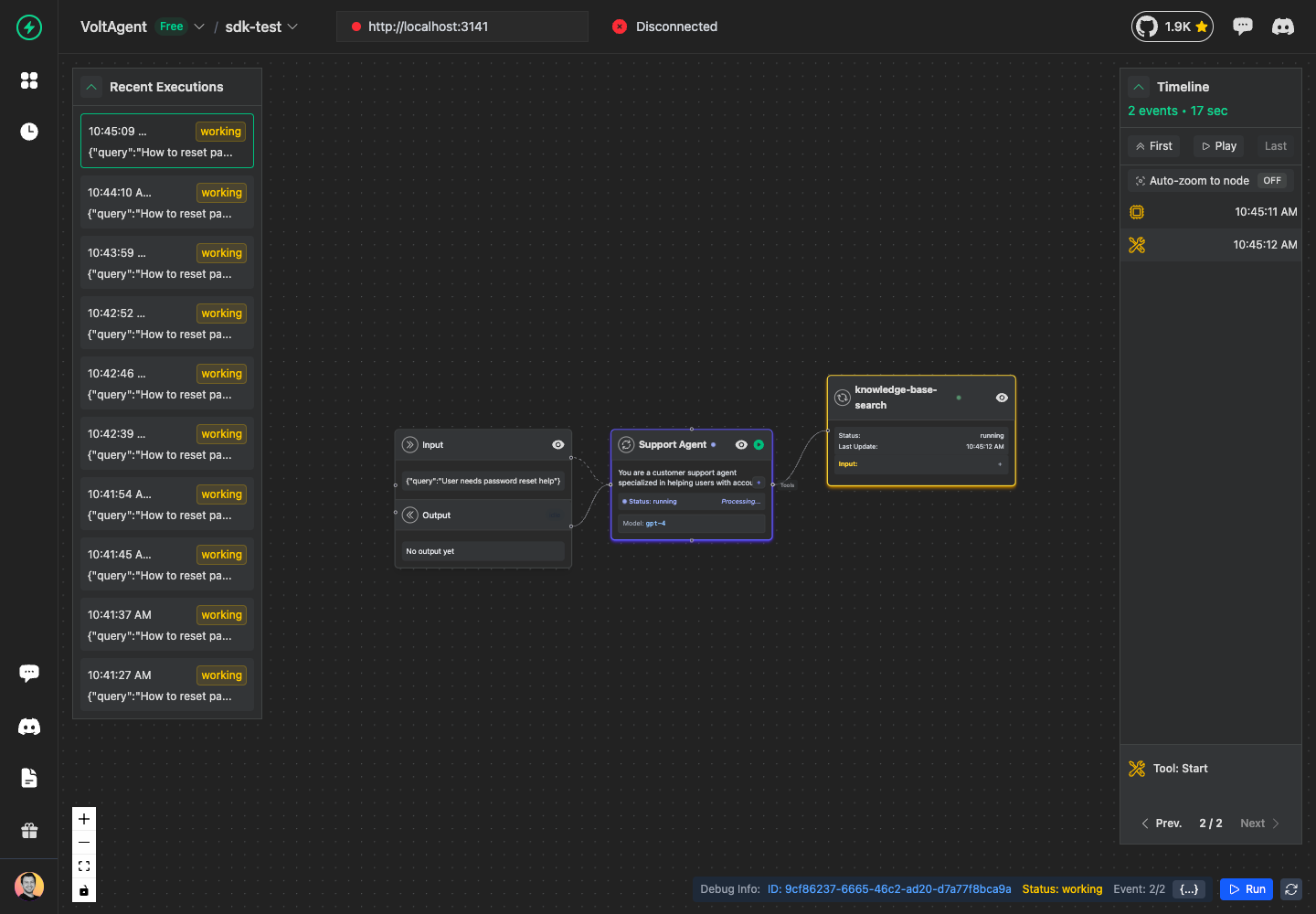
Add a Tool to the Agent
Tools represent external services or APIs that your agent uses. Let's add a knowledge base search tool:
const searchTool = await agent.addTool({
name: "knowledge-base-search",
input: {
query: "password reset procedure",
maxResults: 5,
},
metadata: {
// Add your own custom metadata
searchType: "semantic",
database: "support-kb",
version: "v2",
},
});
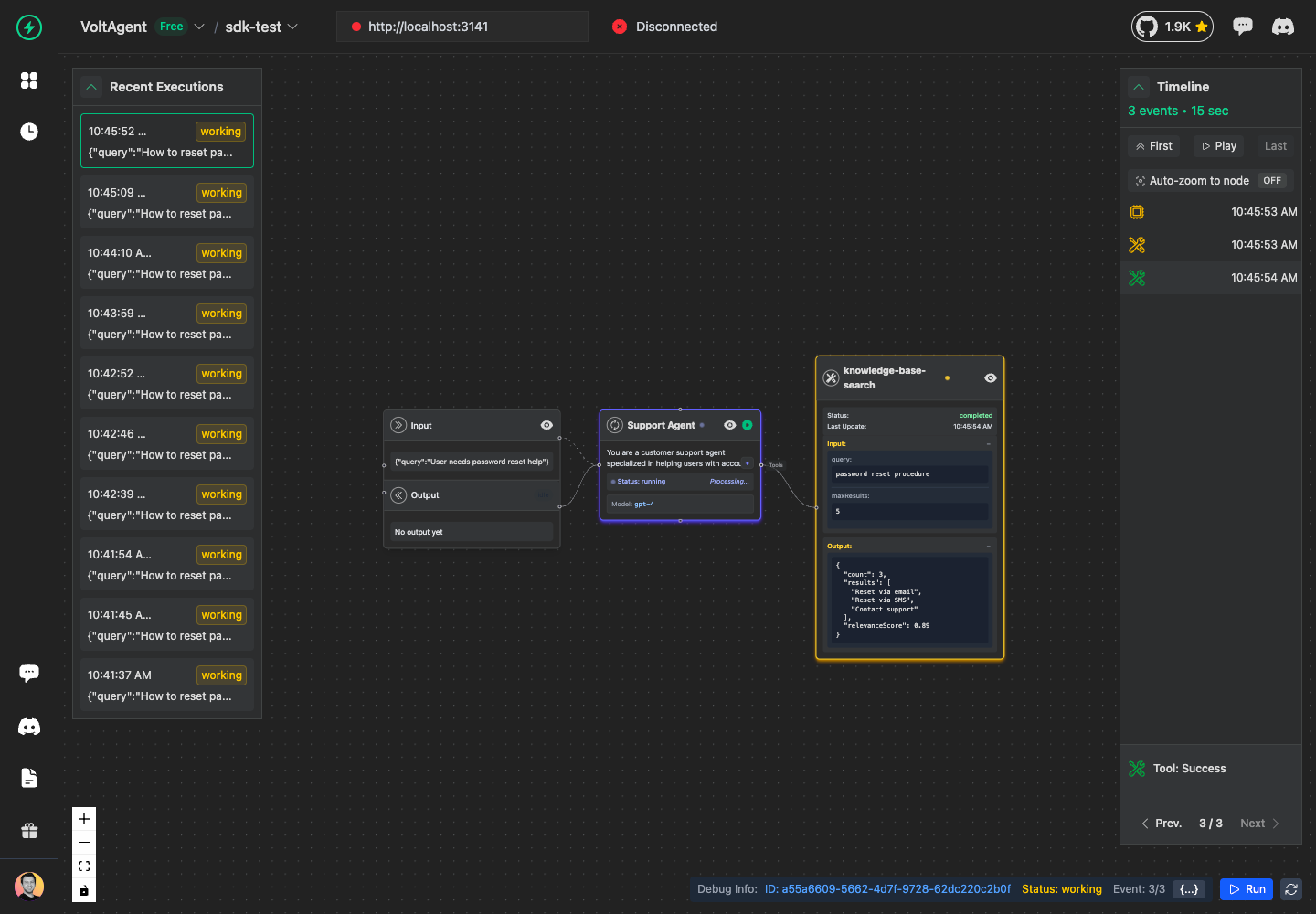
Tool Success
When the tool executes successfully:
await searchTool.success({
output: {
results: ["Reset via email", "Reset via SMS", "Contact support"],
count: 3,
relevanceScore: 0.89,
},
metadata: {
searchTime: "0.2s",
indexUsed: "support-kb-v2",
},
});
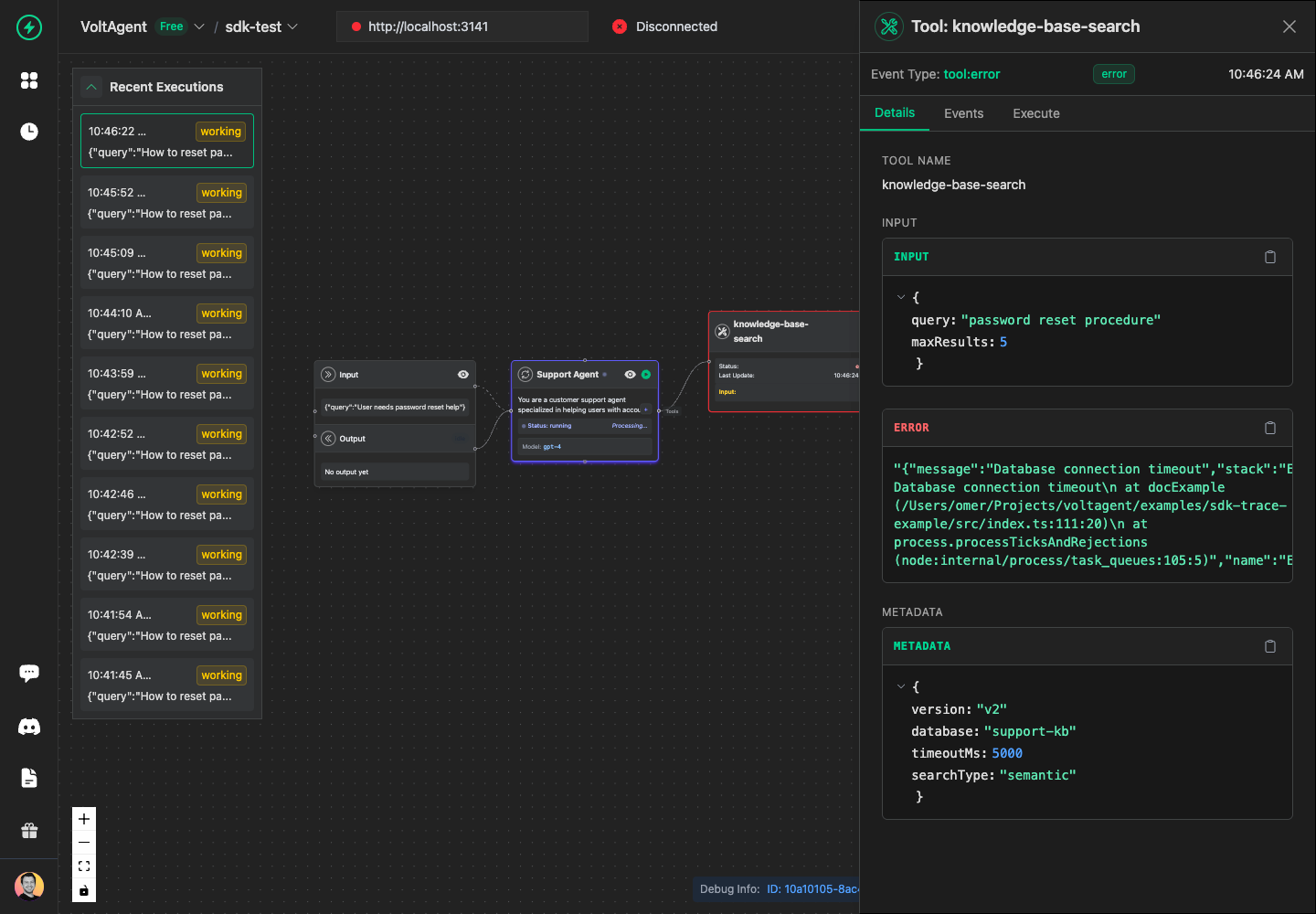
Tool Error
When the tool fails, you can report errors in two ways:
Using Error object:
await searchTool.error({
statusMessage: new Error("Database connection timeout"),
metadata: {
database: "support-kb",
timeoutMs: 5000,
},
});
Using structured error:
await searchTool.error({
statusMessage: {
message: "Database connection timeout",
code: "DB_TIMEOUT",
details: { timeoutMs: 5000 },
},
metadata: {
database: "support-kb",
timeoutMs: 5000,
},
});
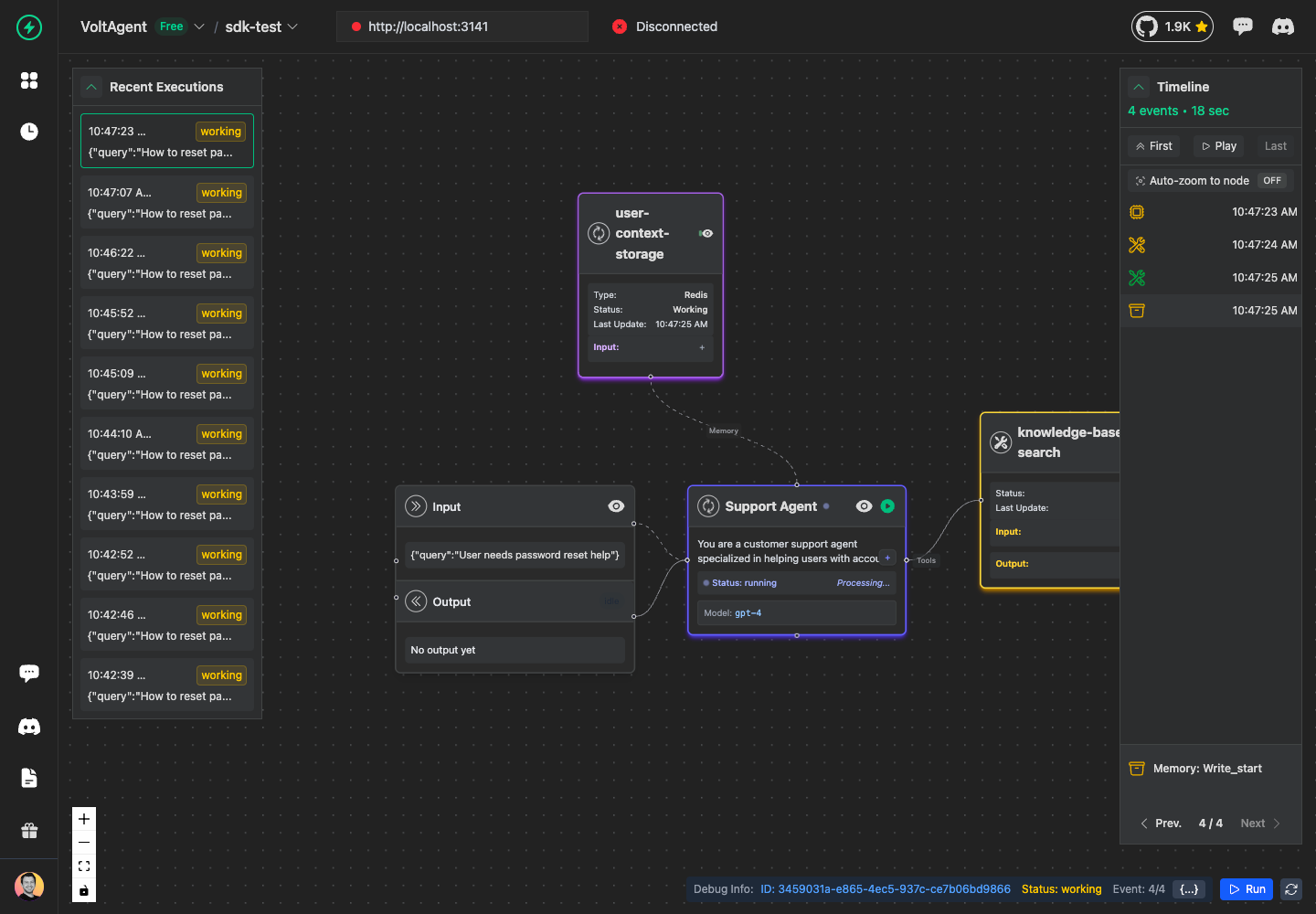
Add Memory Operations
Memory operations track data storage and retrieval. They work exactly like tools with success and error states:
const memoryOp = await agent.addMemory({
name: "user-context-storage",
input: {
key: "user_123_context",
value: {
lastLogin: "2024-01-15",
accountType: "premium",
preferences: { language: "en" },
},
ttl: 3600, // 1 hour
},
metadata: {
type: "redis",
region: "us-east-1",
},
});
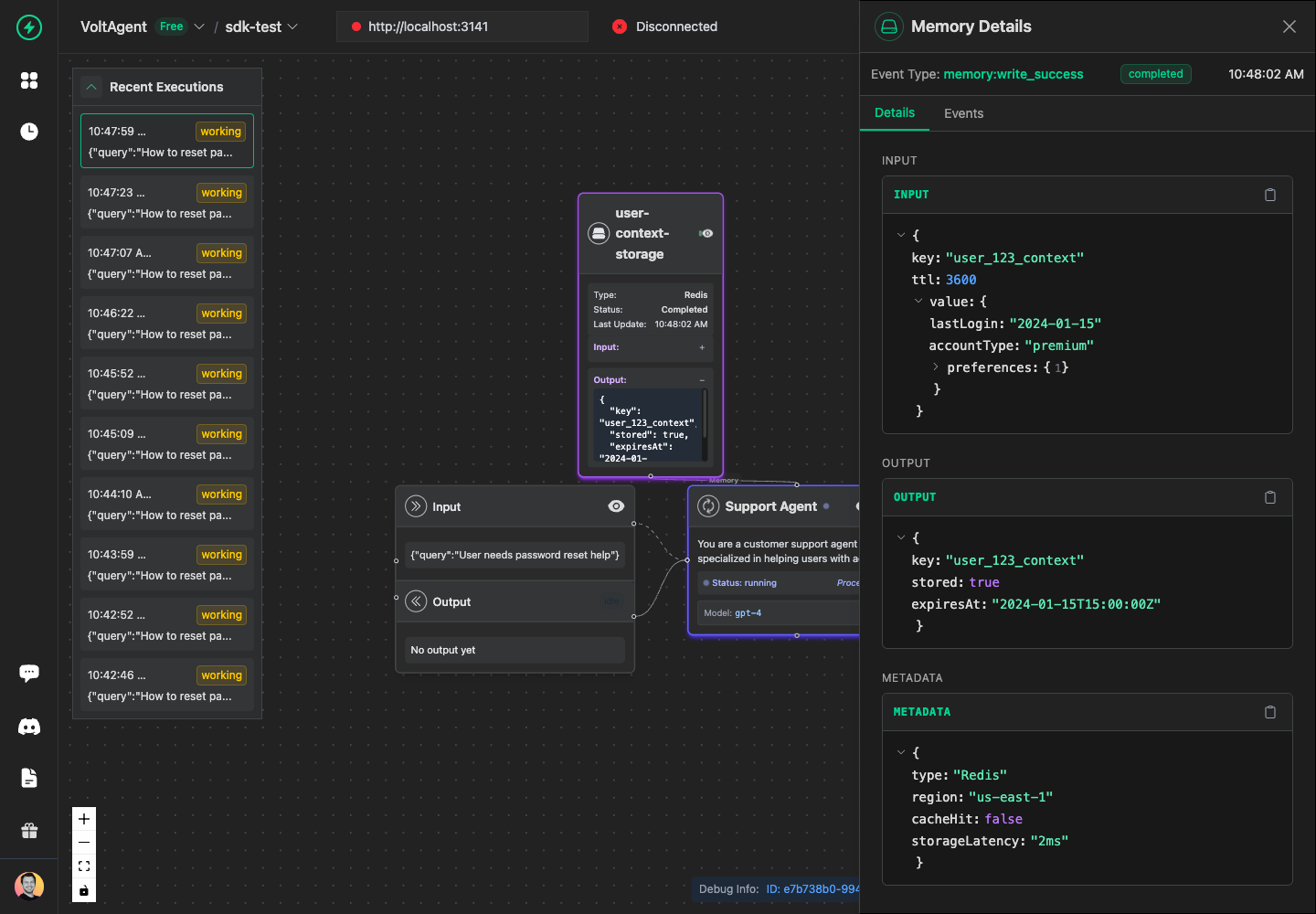
Memory Success
await memoryOp.success({
output: {
stored: true,
key: "user_123_context",
expiresAt: "2024-01-15T15:00:00Z",
},
metadata: {
cacheHit: false,
storageLatency: "2ms",
},
});
Memory Error
await memoryOp.error({
statusMessage: new Error("Redis connection failed"),
metadata: {
storageType: "redis",
errorCode: "CONNECTION_TIMEOUT",
},
});
Add Retrieval Operations
Retrievers handle data retrieval from vector stores, databases, or knowledge bases. They also follow the same success/error pattern:
const retriever = await agent.addRetriever({
name: "policy-document-retriever",
input: {
query: "password reset policy for premium users",
maxDocuments: 3,
threshold: 0.8,
},
metadata: {
vectorStore: "pinecone",
embeddingModel: "text-embedding-ada-002",
},
});
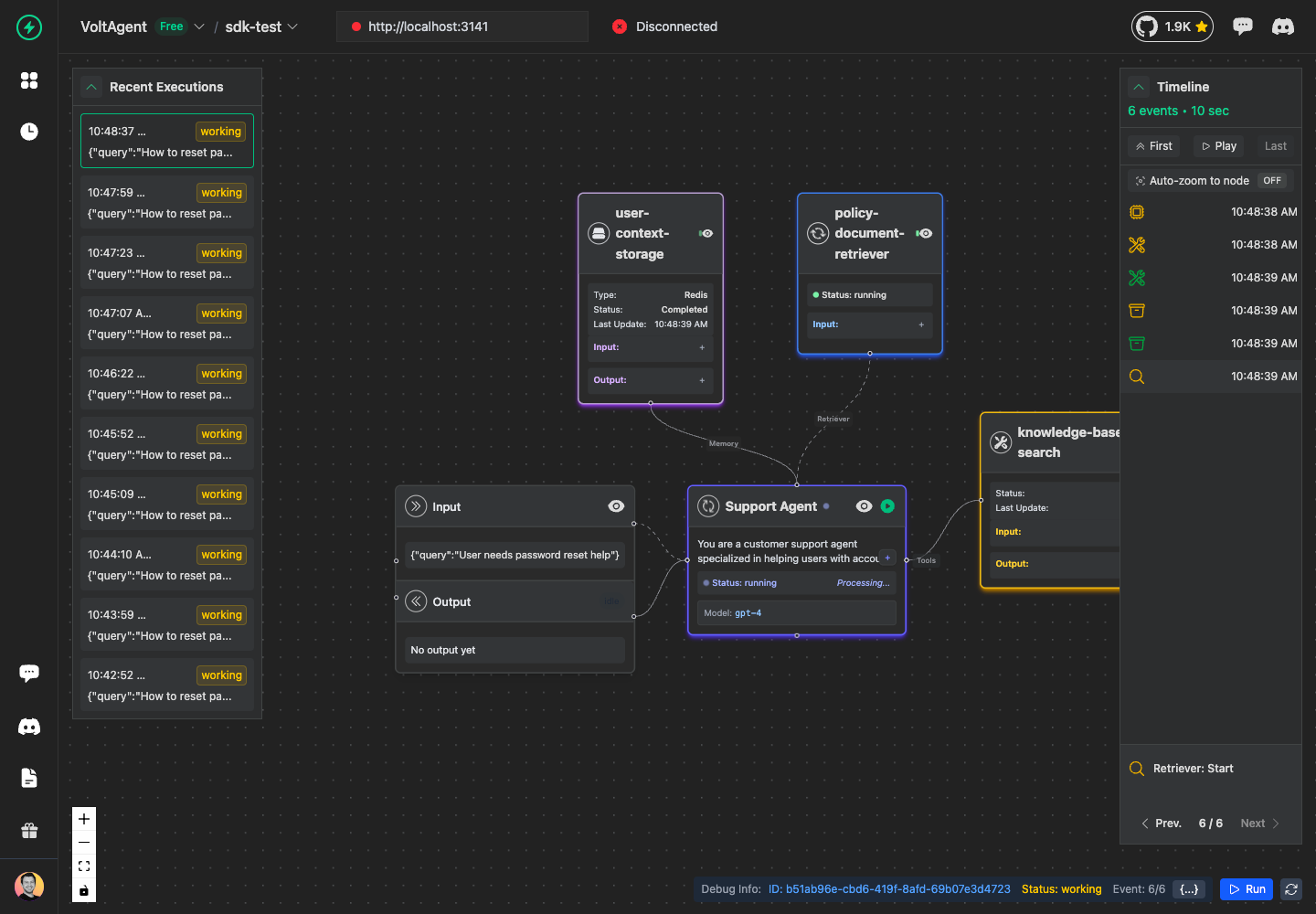
Retriever Success
await retriever.success({
output: {
documents: [
"Premium users can reset passwords instantly via email",
"Password reset requires 2FA verification for premium accounts",
"Premium users have 24/7 phone support for password issues",
],
relevanceScores: [0.95, 0.88, 0.82],
},
metadata: {
searchTime: "0.3s",
documentsScanned: 1500,
},
});
Retriever Error
await retriever.error({
statusMessage: new Error("Vector store unavailable"),
metadata: {
vectorStore: "pinecone",
errorType: "SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE",
},
});
Working with Sub-Agents
Sub-agents create hierarchical agent structures. Each sub-agent can have its own tools, memory operations, and even more sub-agents:
// Create a sub-agent under the main agent
const policyChecker = await agent.addAgent({
name: "Policy Checker",
input: {
userId: "user-123",
requestType: "password-reset",
},
instructions: "You are responsible for verifying customer requests against company policies.",
metadata: {
role: "policy-verification",
modelParameters: {
model: "gpt-4",
},
},
});
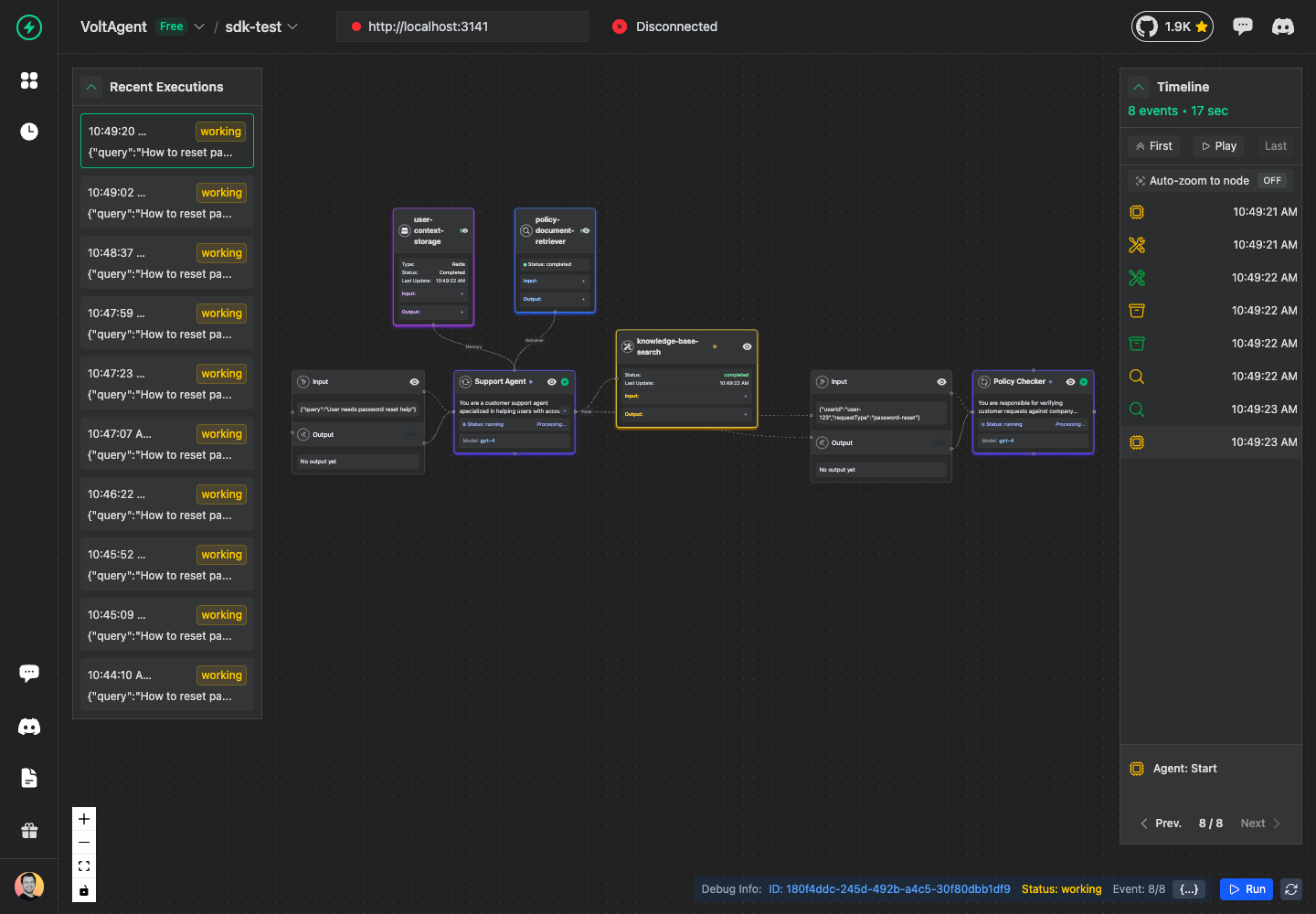
Sub-Agent Success
await policyChecker.success({
output: {
policyCompliant: true,
requiredVerification: "2fa-sms",
approvalGranted: true,
},
usage: {
promptTokens: 85,
completionTokens: 45,
totalTokens: 130,
},
metadata: {
policiesChecked: ["password-policy", "premium-user-policy"],
complianceScore: 0.95,
},
});
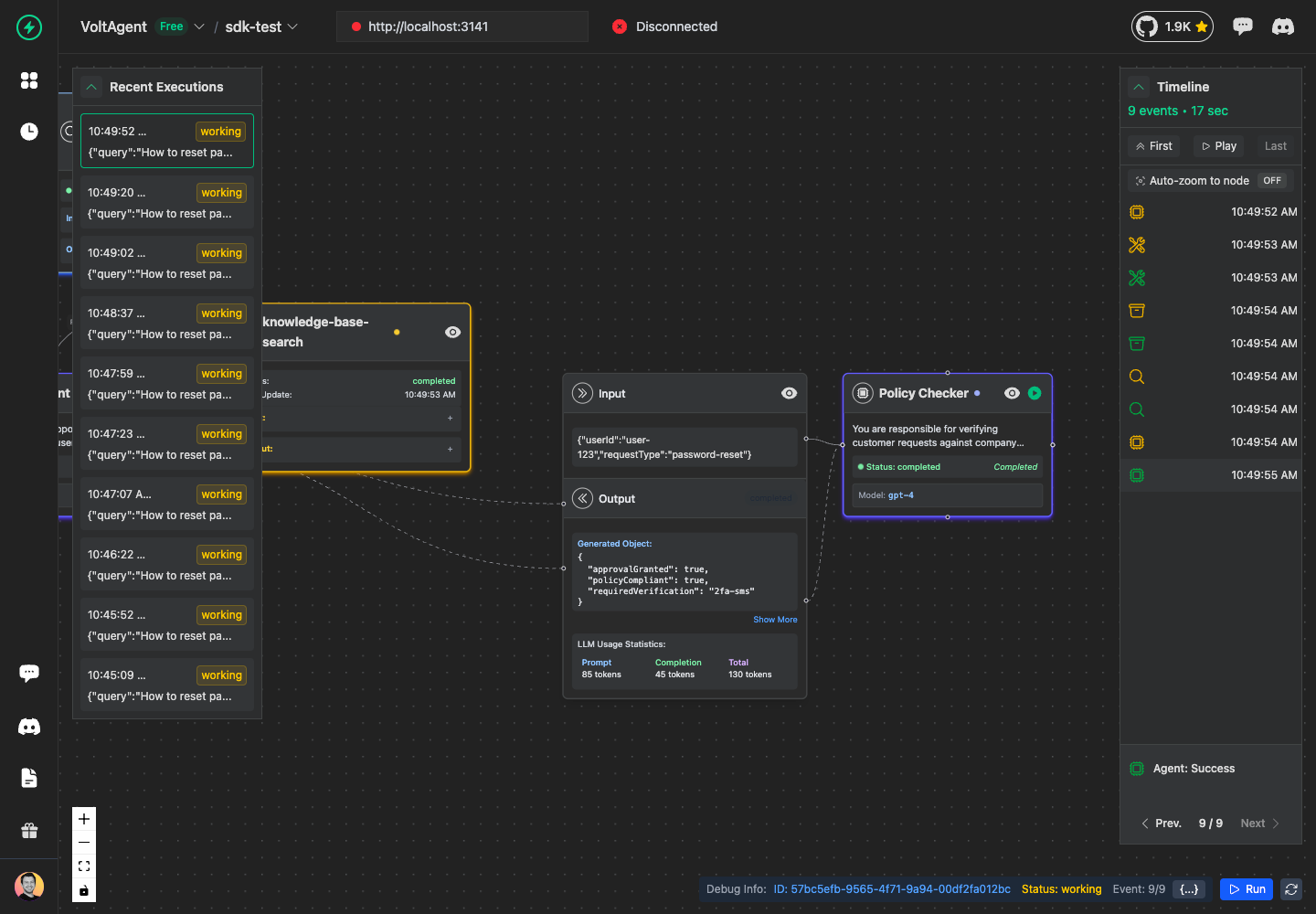
Sub-Agent Error
await policyChecker.error({
statusMessage: new Error("Policy verification failed"),
stage: "policy_check",
metadata: {
failedPolicies: ["premium-user-policy"],
errorCode: "POLICY_VIOLATION",
},
});
Creating Deeper Hierarchies
You can create multiple levels of sub-agents:
// Sub-sub-agent under policy checker
const verifier = await policyChecker.addAgent({
name: "2FA Verifier",
input: { userId: "user-123" },
instructions: "You handle two-factor authentication verification processes.",
metadata: {
role: "two-factor-auth",
modelParameters: {
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
},
},
});
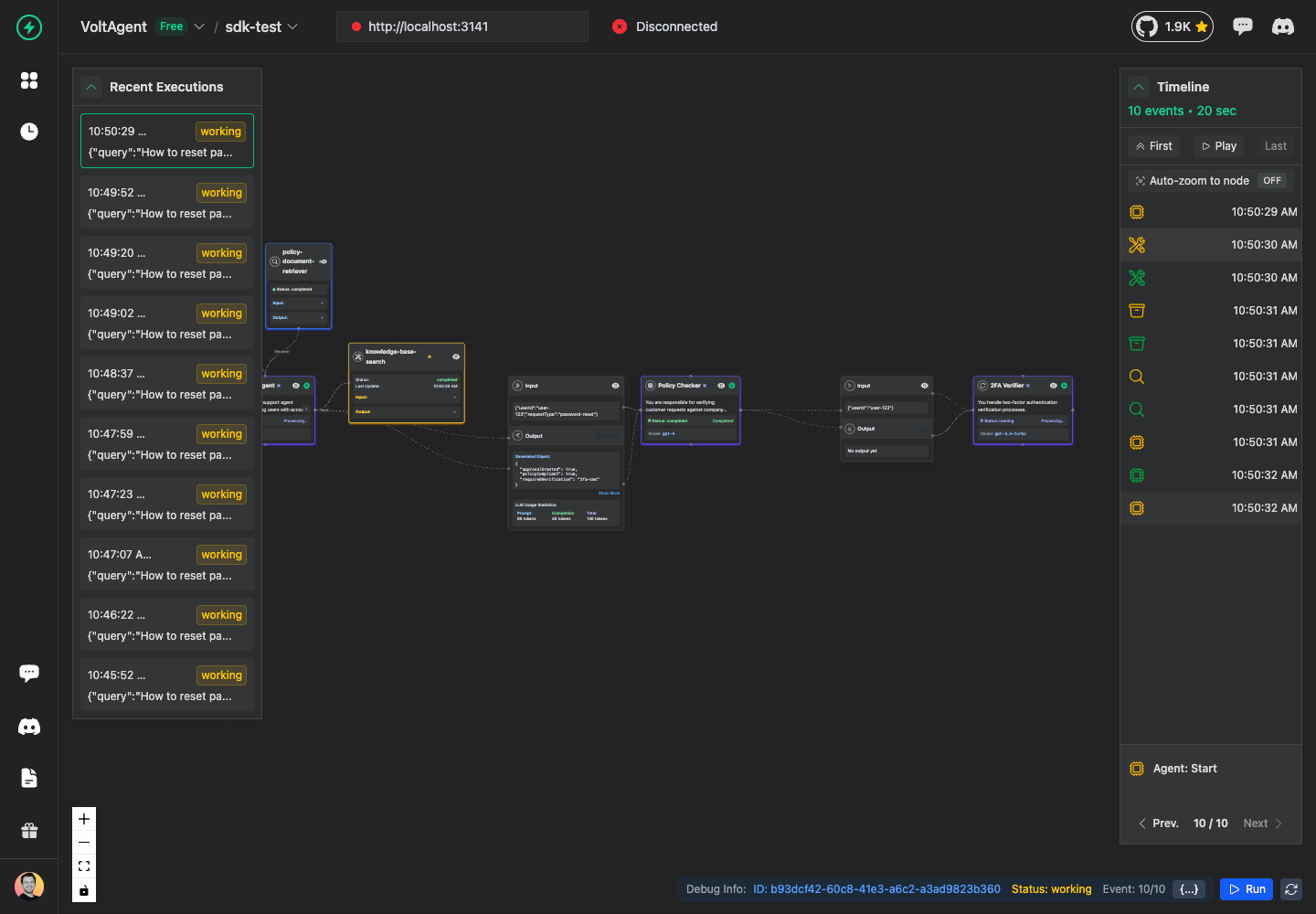
Complete the Agent and Trace
Finally, complete your main agent and trace:
// Complete the main agent
await agent.success({
output: {
response: "Password reset link sent to user's email",
actionTaken: "email-reset-link",
userSatisfied: true,
},
usage: {
promptTokens: 150,
completionTokens: 85,
totalTokens: 235,
},
metadata: {
responseTime: "2.1s",
confidenceScore: 0.95,
},
});
// Complete the trace
await trace.end({
output: {
result: "Customer support query resolved successfully",
resolution: "password-reset-completed",
},
status: "completed",
usage: {
promptTokens: 150,
completionTokens: 85,
totalTokens: 235,
},
metadata: {
totalAgents: 2,
totalOperations: 4,
successRate: 1.0,
},
});
Best Practices
- Always call
sdk.flush()before your application exits - Use meaningful names for traces, agents, tools, and operations
- Include relevant metadata for debugging and analytics
- Track token usage in the
usagefield, not metadata - Handle errors properly with descriptive error messages
- Use hierarchical agents for complex workflows
- Set appropriate tags for easy filtering and search
Complete Example
import { VoltAgentObservabilitySDK } from "@voltagent/sdk";
async function runCompleteExample() {
const sdk = new VoltAgentObservabilitySDK({
baseUrl: process.env.VOLTAGENT_BASE_URL,
publicKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY,
autoFlush: true,
});
try {
// 1. Create trace
const trace = await sdk.trace({
name: "Complete Example",
agentId: "example-agent",
input: { query: "Show me how to use the SDK" },
});
// 2. Add agent
const agent = await trace.addAgent({
name: "Example Agent",
input: { task: "Demonstrate SDK usage" },
instructions: "You demonstrate how to use the VoltAgent SDK effectively.",
metadata: {
modelParameters: { model: "gpt-4" },
},
});
// 3. Add tool
const tool = await agent.addTool({
name: "example-tool",
input: { action: "demonstrate" },
});
await tool.success({
output: { result: "Tool executed successfully" },
});
// 4. Complete agent
await agent.success({
output: { response: "SDK demonstration completed" },
usage: { promptTokens: 50, completionTokens: 30, totalTokens: 80 },
});
// 5. Complete trace
await trace.end({
output: { result: "Example completed successfully" },
status: "completed",
});
await sdk.flush();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Example failed:", error);
} finally {
await sdk.shutdown();
}
}