Memory: Agents That Remember
Learn how to give your agents memory to maintain context across conversations
The Problem: Agents with Amnesia
Your agent can use tools, but every conversation starts from scratch. It can't remember previous interactions, learn from past conversations, or build context over time.
Without Memory
With Memory
Types of Agent Memory
Different types of memory serve different purposes. Let's understand what each one does:
Automatic Memory (Zero Configuration)
.voltagent/memory.db file in your projectCritical: userId Required for Memory
Without a userId, your agent can't properly isolate and store conversations. This is the most common reason why memory "doesn't work" in VoltAgent.
Memory in Action: Test Your Agent
Run your weather agent and test memory functionality. The key is setting a userId - without it, memory won't work properly.
Testing with VoltOps Console
userId to something like "sarah-123"conversationId to "test-memory"See Memory in Action
This demo shows how memory works with proper userId and conversationId settings in VoltOps:
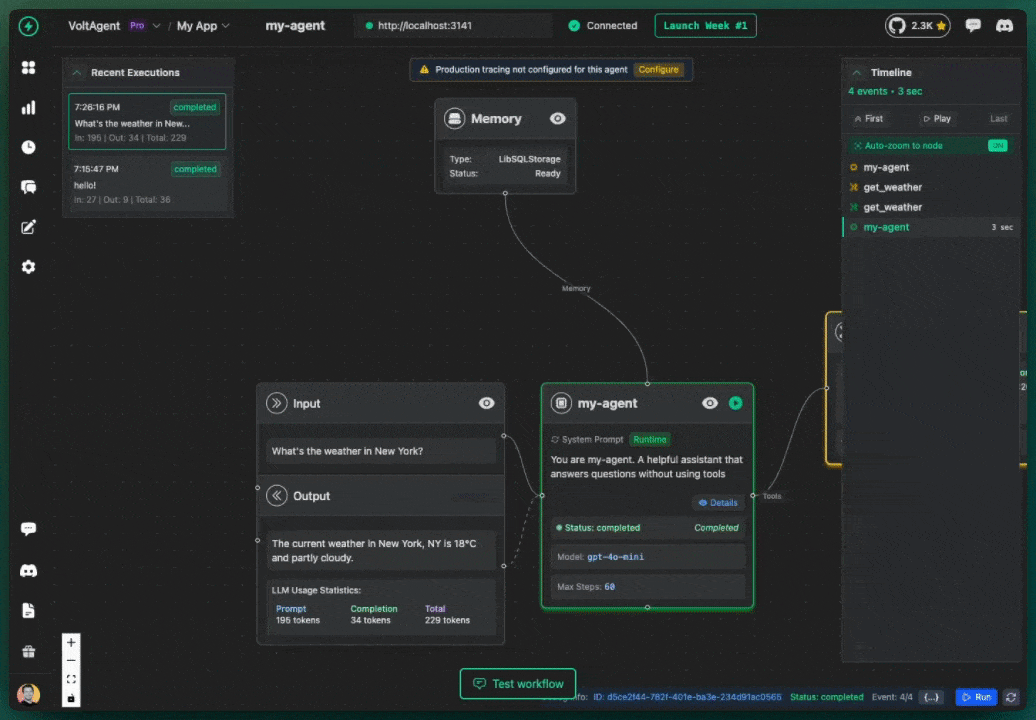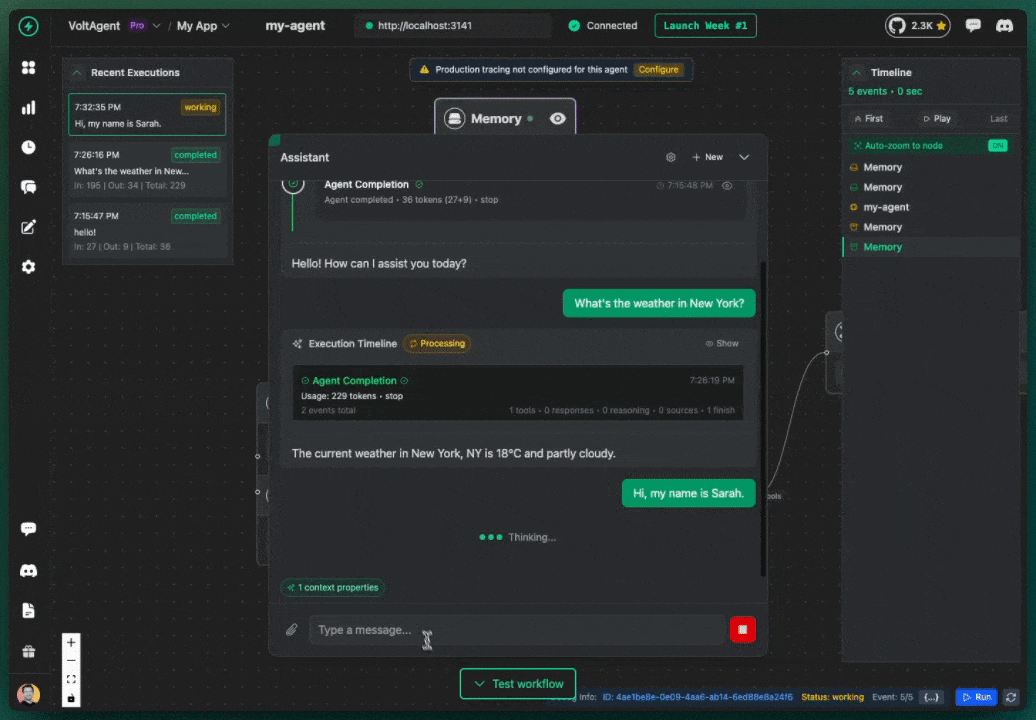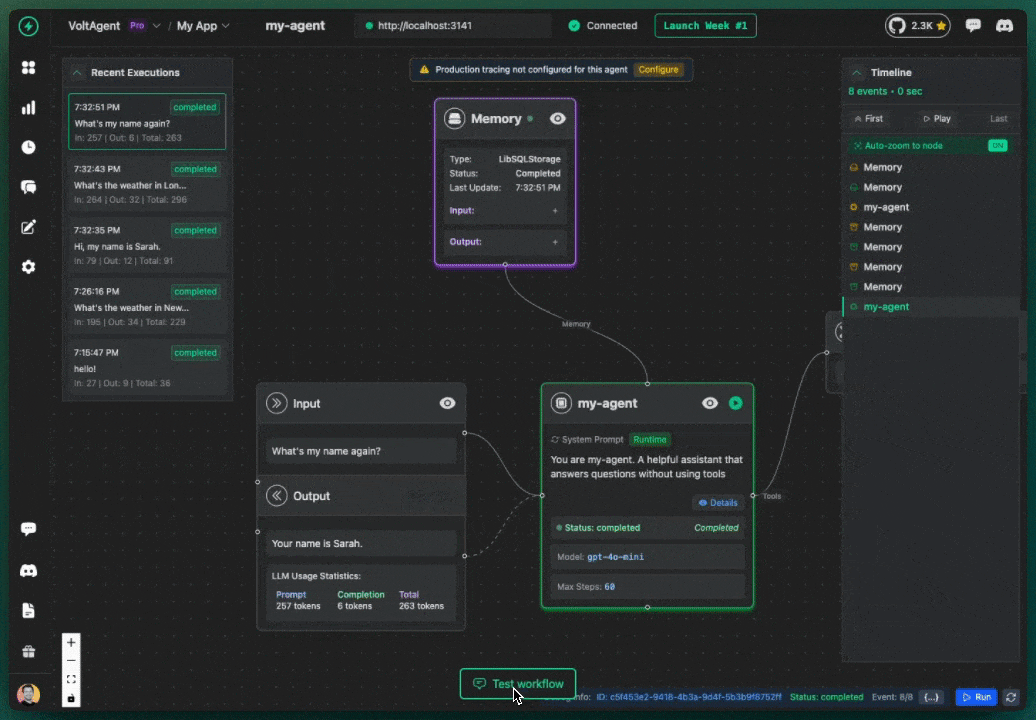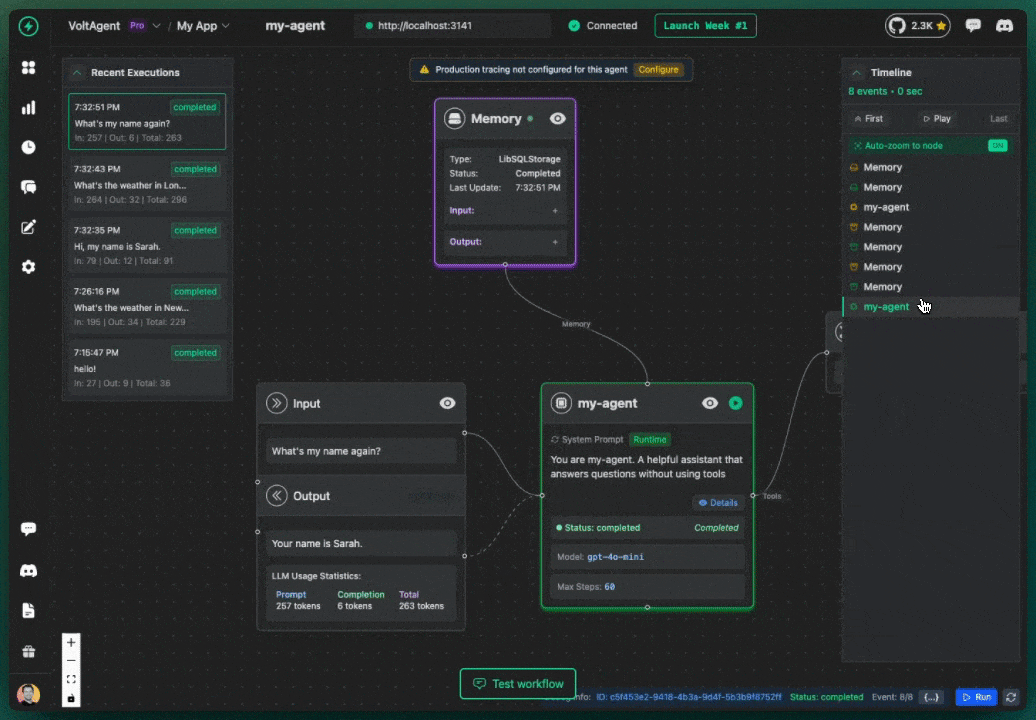
Memory working: Agent remembers the user's name across messages
Test Scenario (with userId set)
The Power of Proper Memory Setup!
With the correct userId and conversationId, your agent now remembers previous conversations and provides a natural, contextual experience. This transforms user experience from robotic to human-like.
User and Conversation IDs
In real applications, you have multiple users and conversations. VoltAgent uses userId and conversationId to keep them separate. userId is mandatory for proper memory functionality.
userId
conversationId
// ❌ WITHOUT userId - Memory won't work properly
const badResponse = await agent.generateText("Hi, my name is Alice.");
// Uses default userId, memory isolation fails
// ✅ WITH userId - Memory works correctly
const response1 = await agent.generateText("Hi, my name is Alice.", {
userId: "alice-123", // REQUIRED for memory to work
conversationId: "chat-session-1" // Optional but recommended
});
const response2 = await agent.generateText("What's my name?", {
userId: "alice-123", // SAME userId = access to memory
conversationId: "chat-session-1" // SAME conversation = full context
});
// Agent: "Your name is Alice!" ✅ Memory working!
// Different user = isolated memory
const response3 = await agent.generateText("Hello, I'm Bob.", {
userId: "bob-456", // DIFFERENT userId = separate memory
conversationId: "chat-session-2"
});
// Same user, new conversation = fresh start but same user profile
const response4 = await agent.generateText("Let's talk about something new.", {
userId: "alice-123", // SAME user
conversationId: "new-topic" // NEW conversation = fresh context
});
Memory Options
VoltAgent offers different memory types. Choose the one that fits your needs.
LibSQLMemoryAdapter (SQLite/Turso)
Default InMemory (no persistence)
PostgreSQL
Supabase
Custom Memory Options
If the default memory isn't enough, you can create your own memory provider.
// Completely disable memory
const statelessAgent = new Agent({
name: "Stateless Agent",
instructions: "This agent remembers nothing.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
memory: false // Memory disabled
});
import { InMemoryStorage } from "@voltagent/core";
const fastAgent = new Agent({
name: "Fast Agent",
instructions: "This agent stores memory in RAM.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
memory: new InMemoryStorage()
});
import { PostgreSQLStorage } from "@voltagent/postgres";
const productionAgent = new Agent({
name: "Production Agent",
instructions: "This agent stores memory in PostgreSQL.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
memory: new PostgreSQLStorage({
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL
})
});
Best Practices
Follow these tips to use memory effectively.
Do This
Don't Do This
Using Memory via REST API
If you're building a web app or mobile app, you'll likely call your VoltAgent via REST API. Here's how to properly set userId and conversationId in API calls.
API Server URL
Your VoltAgent automatically starts an API server on port 3141 (or another available port):
# ❌ Without userId - Memory won't work
curl -X POST http://localhost:3141/agents/my-agent/text \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "Hi, my name is Sarah. What's the weather like?"
}'
# ✅ With userId and conversationId - Memory works!
curl -X POST http://localhost:3141/agents/my-agent/text \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "Hi, my name is Sarah. What\'s the weather like?",
"options": {
"userId": "sarah-123",
"conversationId": "weather-chat-001"
}
}'
# Follow-up message in same conversation
curl -X POST http://localhost:3141/agents/my-agent/text \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "What was my name again?",
"options": {
"userId": "sarah-123",
"conversationId": "weather-chat-001"
}
}'
# Response: "Your name is Sarah!" ✅
// Frontend code example
const userId = getCurrentUserId(); // Get from your auth system
const conversationId = generateConversationId(); // Generate or get existing
async function chatWithAgent(message) {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:3141/agents/my-agent/text', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
input: message,
options: {
userId: userId, // REQUIRED for memory
conversationId: conversationId, // Optional but recommended
temperature: 0.7,
maxTokens: 500
}
})
});
const result = await response.json();
return result.data;
}
// Usage
await chatWithAgent("Hi, I'm Sarah. What's the weather?");
await chatWithAgent("What's my name?"); // Will remember "Sarah"
Key Points for API Usage
userId in the options objectuserId for the same user across all requestsconversationId to maintain conversation contextconversationId for new conversation threads