VoltAgent Server API
VoltAgent provides a flexible HTTP API for interacting with agents and workflows. The server architecture is framework-agnostic, allowing you to use different server implementations or create your own.
Architecture
VoltAgent 1.x introduces a pluggable server architecture:
@voltagent/server-core- Framework-agnostic core with route definitions, handlers, and base provider@voltagent/server-hono- Official server implementation using Hono (recommended)@voltagent/server-elysia- High-performance server implementation using Elysia
Quick Start
Using Hono (Recommended)
import { Agent, VoltAgent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { honoServer } from "@voltagent/server-hono";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Assistant",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
});
new VoltAgent({
agents: { agent },
server: honoServer({
port: 3141,
enableSwaggerUI: true,
}),
});
Using Elysia
import { Agent, VoltAgent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { elysiaServer } from "@voltagent/server-elysia";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Assistant",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
});
new VoltAgent({
agents: { agent },
server: elysiaServer({
port: 3141,
enableSwaggerUI: true,
}),
});
You can also set model to a string like openai/gpt-4o-mini instead of importing a provider package.
The server starts automatically and displays:
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
VOLTAGENT SERVER STARTED SUCCESSFULLY
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
✓ HTTP Server: http://localhost:3141
↪ Share it: pnpm volt tunnel 3141 (secure HTTPS tunnel for teammates)
Docs: https://voltagent.dev/deployment-docs/local-tunnel/
✓ Swagger UI: http://localhost:3141/ui
Test your agents with VoltOps Console: https://console.voltagent.dev
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
API Documentation
Interactive Documentation
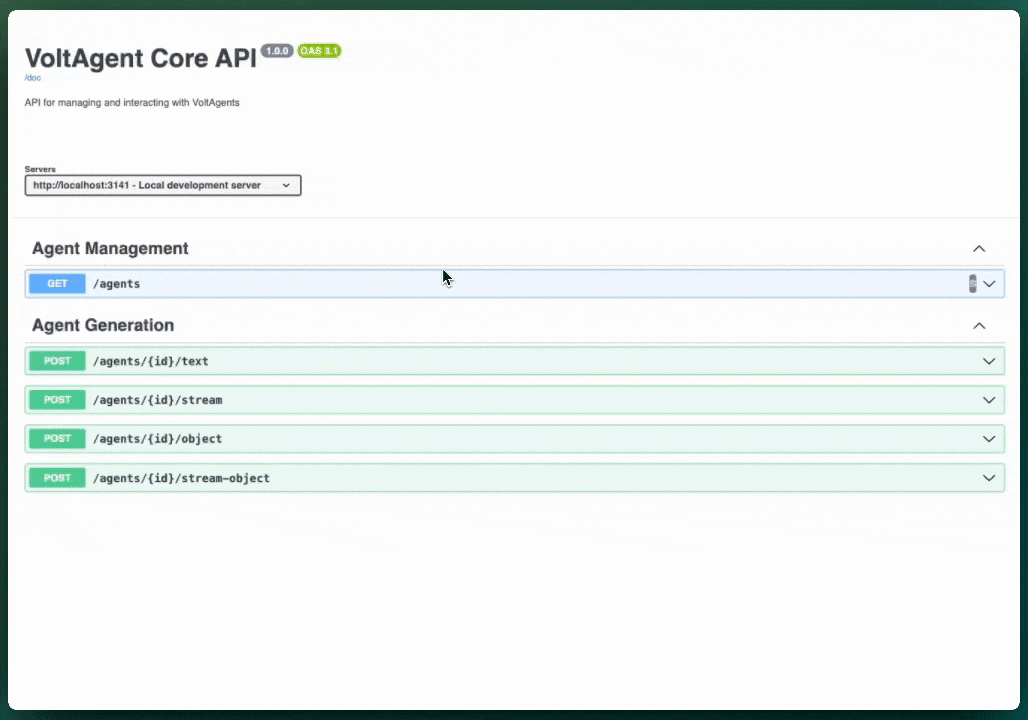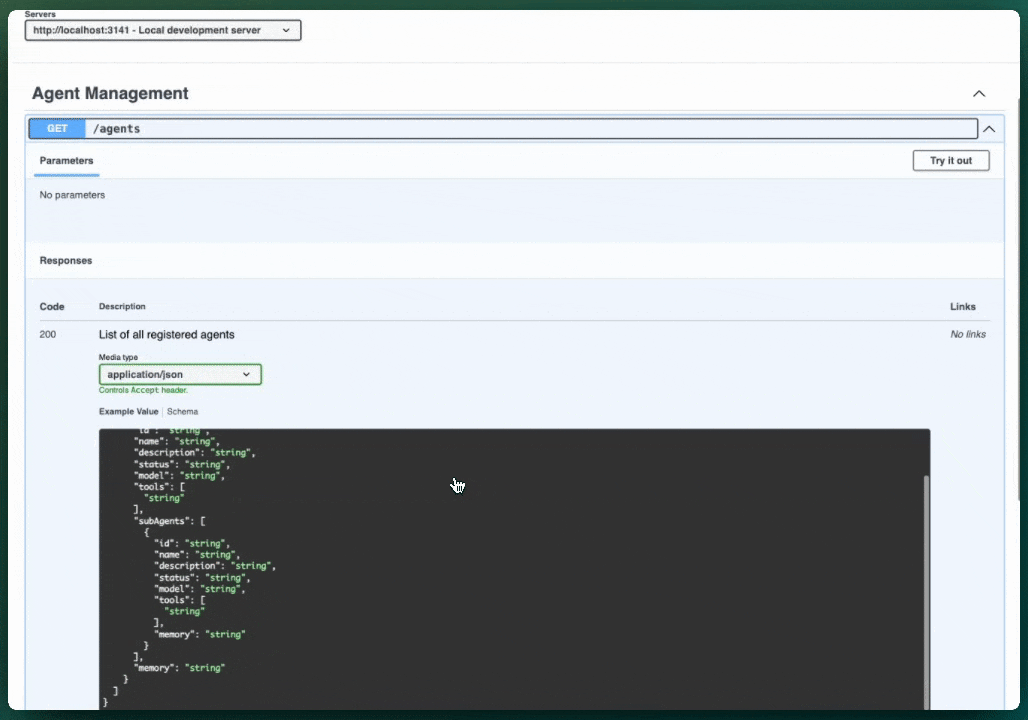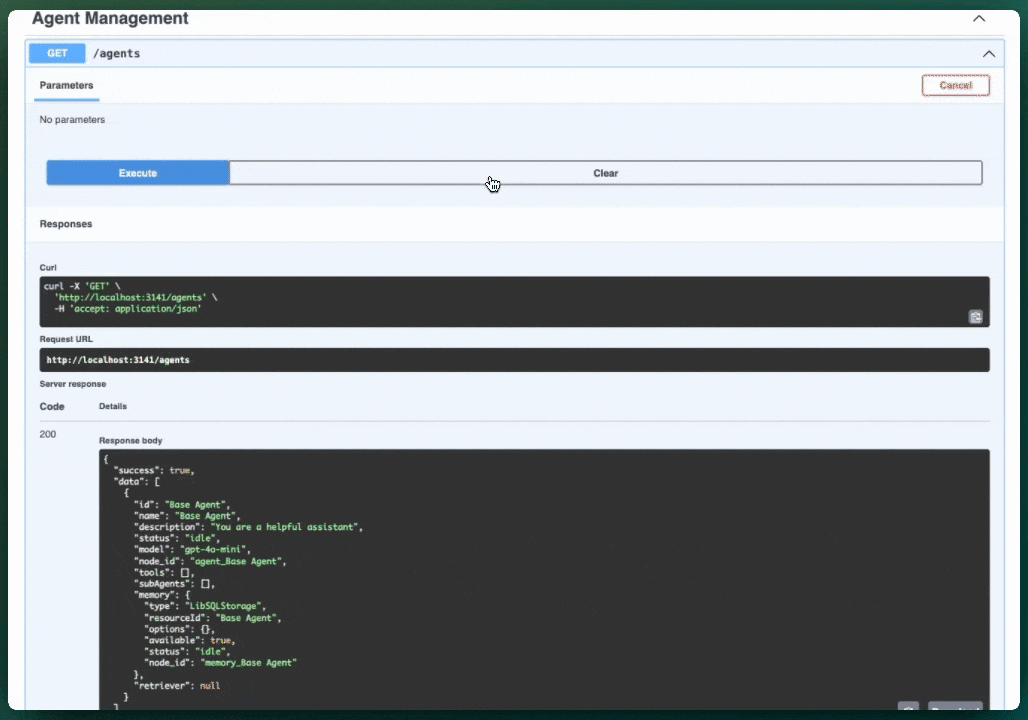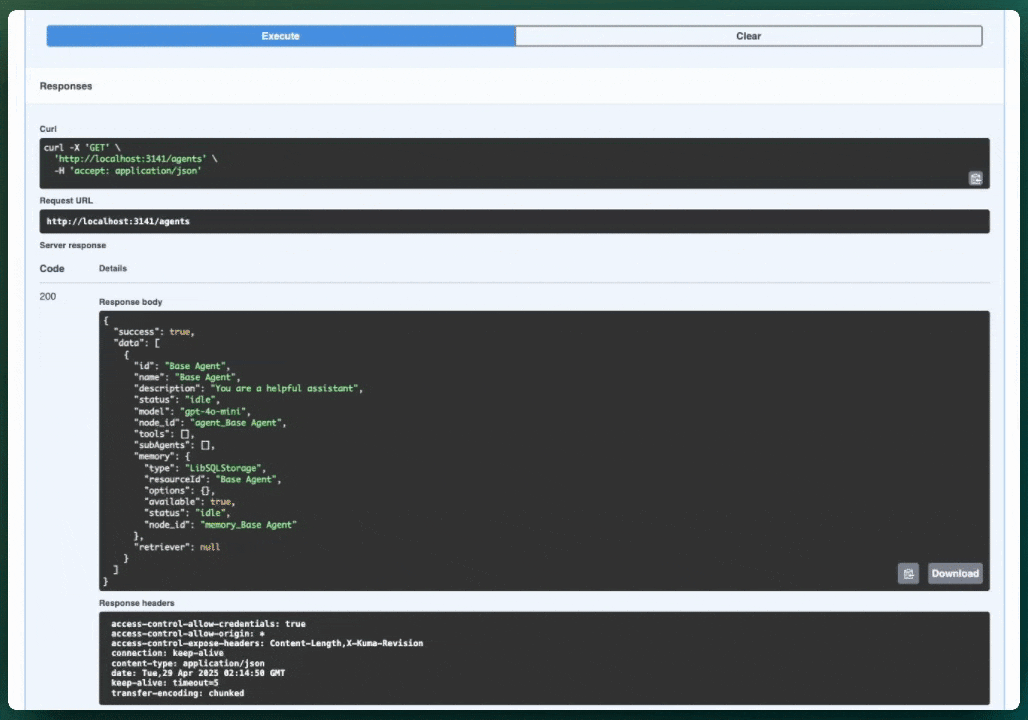
Access Swagger UI at http://localhost:3141/ui to explore and test all endpoints directly in your browser.
OpenAPI Specification
Get the raw OpenAPI 3.1 spec at http://localhost:3141/doc for code generation and tooling.
Core Endpoints
Agent Endpoints
GET /agents- List all agentsPOST /agents/:id/text- Generate text responsePOST /agents/:id/stream- Stream text response (SSE)POST /agents/:id/object- Generate structured objectPOST /agents/:id/stream-object- Stream structured object (SSE)GET /agents/:id/history- Get agent execution history
Workflow Endpoints
GET /workflows- List all workflowsGET /workflows/executions- List workflow executions (filters via query params;workflowIdoptional)POST /workflows/:id/execute- Execute workflowPOST /workflows/:id/stream- Stream workflow execution (SSE)POST /workflows/:id/executions/:executionId/suspend- Suspend executionPOST /workflows/:id/executions/:executionId/resume- Resume executionGET /workflows/:id/executions/:executionId/state- Get execution state
Tool Endpoints
GET /tools- List all registered tools (across agents)POST /tools/:name/execute- Execute a tool directly over HTTP
Memory Endpoints
GET /api/memory/conversations- List conversationsGET /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId- Get conversationGET /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId/messages- List messagesGET /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId/working-memory- Get working memoryPOST /api/memory/save-messages- Save messagesPOST /api/memory/conversations- Create conversationPATCH /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId- Update conversationDELETE /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId- Delete conversationPOST /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId/clone- Clone conversationPOST /api/memory/conversations/:conversationId/working-memory- Update working memoryPOST /api/memory/messages/delete- Delete messagesGET /api/memory/search- Search memory
Observability & Logs
POST /setup-observability- Configure.envwith VoltAgent keysGET /observability/status- Observability statusGET /observability/traces- List tracesGET /observability/traces/:traceId- Get trace by IDGET /observability/spans/:spanId- Get span detailsGET /observability/traces/:traceId/logs- Logs for a traceGET /observability/spans/:spanId/logs- Logs for a spanGET /observability/logs- Query logs (filters)GET /api/logs- System logs (filters)
System
GET /updates- Check available updatesPOST /updates- Install updates (all or a specific package)
Documentation Sections
- Server Architecture - Understanding the pluggable server design
- Agent Endpoints - Complete agent API reference with examples
- Workflow Endpoints - Workflow execution and management
- Memory Endpoints - Conversation and message storage APIs
- Authentication - Securing your API endpoints
- Streaming - Real-time features with SSE and WebSocket
- Custom Endpoints - Adding your own REST endpoints
- API Reference - Complete endpoint reference
Next Steps
- Explore the Server Architecture to understand how VoltAgent servers work
- Check Agent Endpoints for detailed API usage
- Visit
/uion your running server for interactive API exploration