VoltAgent with Pinecone
Pinecone is a fully managed vector database built for machine learning applications that require fast, accurate vector search at scale. It offers serverless deployment, automatic scaling, and enterprise-grade security.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Node.js 18+ installed
- Pinecone account (free tier available)
- Pinecone API key
- OpenAI API key (for embeddings)
Installation
Create a new VoltAgent project with Pinecone integration:
npm create voltagent-app@latest -- --example with-pinecone
cd with-pinecone
This creates a complete VoltAgent + Pinecone setup with sample data and two different agent configurations.
Install the dependencies:
- npm
- pnpm
- yarn
npm install
pnpm install
yarn install
Environment Setup
Create a .env file with your configuration:
# Pinecone API key from https://app.pinecone.io/
PINECONE_API_KEY=your-pinecone-api-key-here
# OpenAI API key for embeddings and LLM
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-here
Getting Your Pinecone API Key
- Sign up for a free account at pinecone.io
- Navigate to the Pinecone console
- Go to "API Keys" in the sidebar
- Create a new API key or copy your existing one
Run Your Application
Start your VoltAgent application:
- npm
- pnpm
- yarn
npm run dev
pnpm dev
yarn dev
You'll see:
🚀 VoltAgent with Pinecone is running!
📋 Creating new index "voltagent-knowledge-base"...
✅ Index "voltagent-knowledge-base" created successfully
📚 Populating index with sample documents...
✅ Successfully upserted 5 documents to index
📚 Two different agents are ready:
1️⃣ Assistant with Retriever - Automatic semantic search on every interaction
2️⃣ Assistant with Tools - LLM decides when to search autonomously
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
VOLTAGENT SERVER STARTED SUCCESSFULLY
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
✓ HTTP Server: http://localhost:3141
↪ Share it: pnpm volt tunnel 3141 (secure HTTPS tunnel for teammates)
Docs: https://voltagent.dev/deployment-docs/local-tunnel/
✓ Swagger UI: http://localhost:3141/ui
Test your agents with VoltOps Console: https://console.voltagent.dev
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
Interact with Your Agents
Your agents are now running! To interact with them:
- Open the Console: Click the
https://console.voltagent.devlink in your terminal output (or copy-paste it into your browser). - Find Your Agents: On the VoltOps LLM Observability Platform page, you should see both agents listed:
- "Assistant with Retriever"
- "Assistant with Tools"
- Open Agent Details: Click on either agent's name.
- Start Chatting: On the agent detail page, click the chat icon in the bottom right corner to open the chat window.
- Test RAG Capabilities: Try questions like:
- "What is VoltAgent?"
- "Tell me about Pinecone"
- "How does vector search work?"
- "What is RAG?"
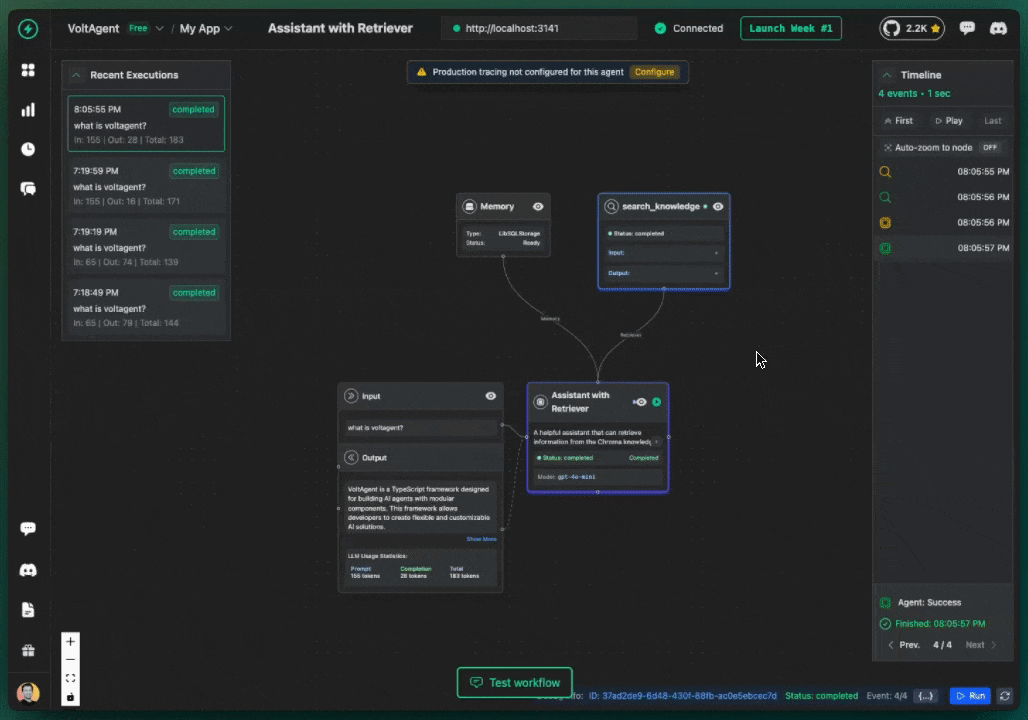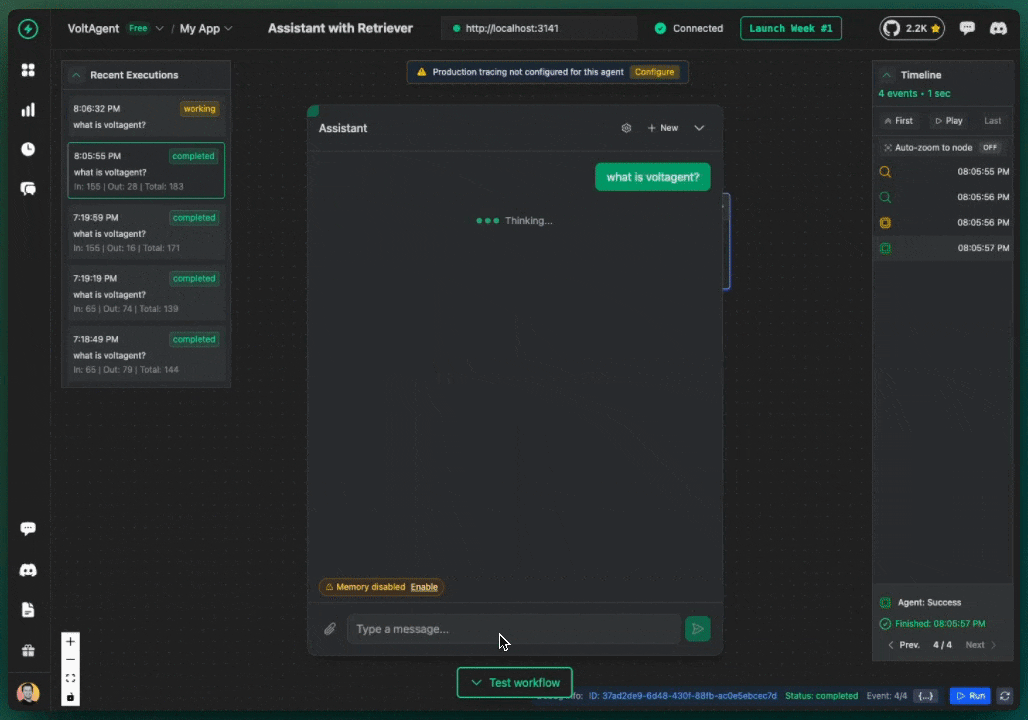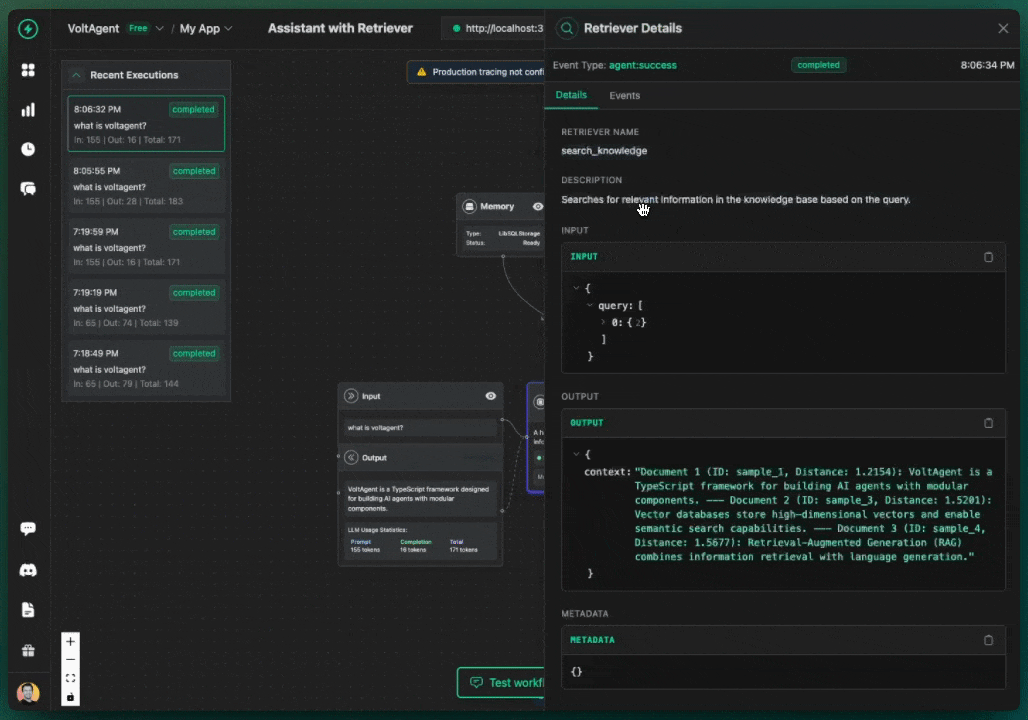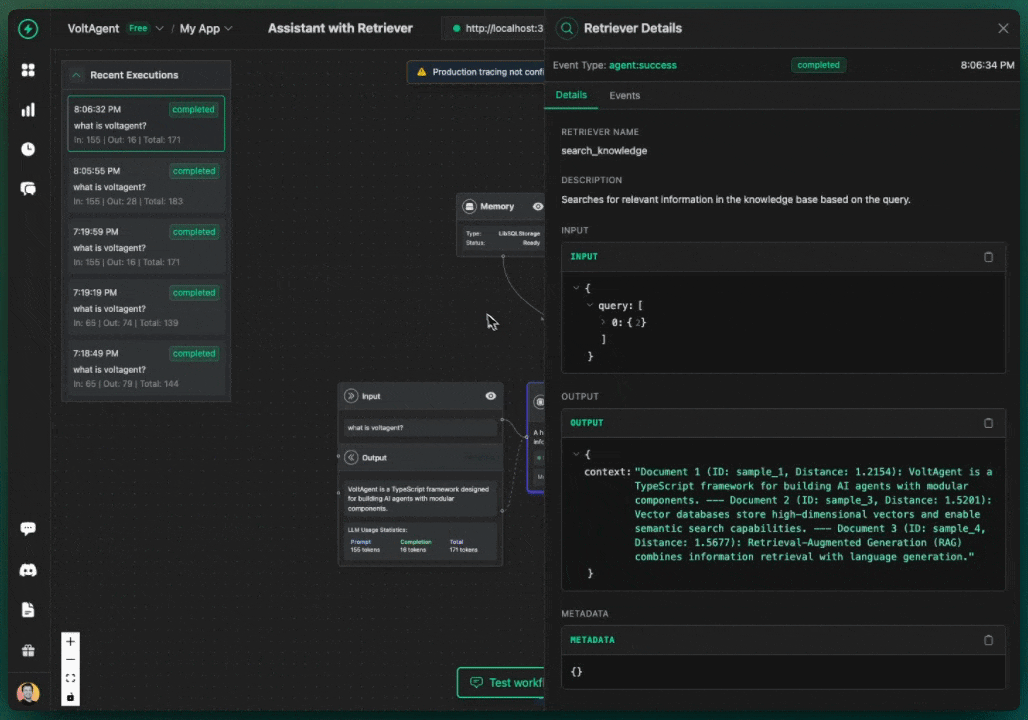
You should receive responses from your AI agents that include relevant information from your Pinecone knowledge base, along with source references showing which documents were used to generate the response.
How It Works
The following sections explain how this example is built and how you can customize it.
Create the Pinecone Retriever
Create src/retriever/index.ts:
import { BaseRetriever, type BaseMessage, type RetrieveOptions } from "@voltagent/core";
import { Pinecone } from "@pinecone-database/pinecone";
// Initialize Pinecone client
const pc = new Pinecone({
apiKey: process.env.PINECONE_API_KEY!,
sourceTag: "voltagent",
});
const indexName = "voltagent-knowledge-base";
Key Components Explained:
- Pinecone Client: Connects to Pinecone's managed service
- Index: A named container for your vectors in Pinecone
- Serverless Architecture: Automatically scales based on usage
Initialize Index and Sample Data
The example automatically creates and populates your Pinecone index:
async function initializeIndex() {
try {
// Check if index exists
let indexExists = false;
try {
await pc.describeIndex(indexName);
indexExists = true;
} catch (error) {
console.log(`📋 Creating new index "${indexName}"...`);
}
// Create index if it doesn't exist
if (!indexExists) {
await pc.createIndex({
name: indexName,
dimension: 1536, // OpenAI text-embedding-3-small dimension
metric: "cosine",
spec: {
serverless: {
cloud: "aws",
region: "us-east-1",
},
},
waitUntilReady: true,
});
}
// Get the index and populate with sample data
const index = pc.index(indexName);
const stats = await index.describeIndexStats();
if (stats.totalRecordCount === 0) {
// Generate embeddings and upsert documents
await populateWithSampleData(index);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error initializing Pinecone index:", error);
}
}
What This Does:
- Creates a serverless Pinecone index in AWS us-east-1
- Uses cosine similarity for vector comparisons
- Automatically populates with sample documents
- Generates embeddings using OpenAI's API
Implement the Retriever Class
Create the main retriever class:
async function retrieveDocuments(query: string, topK = 3) {
try {
// Generate embedding for the query
const OpenAI = await import("openai");
const openai = new OpenAI.default({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY!,
});
const embeddingResponse = await openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-3-small",
input: query,
});
const queryVector = embeddingResponse.data[0].embedding;
// Search the index
const index = pc.index(indexName);
const searchResults = await index.query({
vector: queryVector,
topK,
includeMetadata: true,
includeValues: false,
});
// Format results
return (
searchResults.matches?.map((match) => ({
content: match.metadata?.text || "",
metadata: match.metadata || {},
score: match.score || 0,
id: match.id,
})) || []
);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving documents:", error);
return [];
}
}
export class PineconeRetriever extends BaseRetriever {
async retrieve(input: string | BaseMessage[], options: RetrieveOptions): Promise<string> {
// Convert input to searchable string
let searchText = "";
if (typeof input === "string") {
searchText = input;
} else if (Array.isArray(input) && input.length > 0) {
const lastMessage = input[input.length - 1];
if (Array.isArray(lastMessage.content)) {
const textParts = lastMessage.content
.filter((part: any) => part.type === "text")
.map((part: any) => part.text);
searchText = textParts.join(" ");
} else {
searchText = lastMessage.content as string;
}
}
// Perform semantic search
const results = await retrieveDocuments(searchText, 3);
// Add references to context for tracking
if (options.context && results.length > 0) {
const references = results.map((doc: any, index: number) => ({
id: doc.id,
title: doc.metadata.topic || `Document ${index + 1}`,
source: "Pinecone Knowledge Base",
score: doc.score,
category: doc.metadata.category,
}));
options.context.set("references", references);
}
// Format results for the LLM
if (results.length === 0) {
return "No relevant documents found in the knowledge base.";
}
return results
.map(
(doc: any, index: number) =>
`Document ${index + 1} (ID: ${doc.id}, Score: ${doc.score.toFixed(4)}, Category: ${doc.metadata.category}):\n${doc.content}`
)
.join("\n\n---\n\n");
}
}
export const retriever = new PineconeRetriever();
Key Features:
- Input Handling: Supports both string and message array inputs
- Embedding Generation: Uses OpenAI's embedding API
- Vector Search: Leverages Pinecone's optimized search
- User Context: Tracks references and similarity scores
- Error Handling: Graceful fallbacks for search failures
Create Your Agents
Now create agents using different retrieval patterns in src/index.ts:
import { Agent, VoltAgent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { honoServer } from "@voltagent/server-hono";
import { retriever } from "./retriever/index.js";
// Agent 1: Automatic retrieval on every interaction
const agentWithRetriever = new Agent({
name: "Assistant with Retriever",
instructions:
"A helpful assistant that automatically searches the Pinecone knowledge base for relevant information",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
retriever: retriever,
});
// Agent 2: LLM decides when to search
const agentWithTools = new Agent({
name: "Assistant with Tools",
instructions: "A helpful assistant that can search the knowledge base when needed",
model: "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
tools: [retriever.tool],
});
new VoltAgent({
agents: {
agentWithRetriever,
agentWithTools,
},
server: honoServer(),
});
Usage Patterns
Automatic Retrieval
The first agent automatically searches before every response:
User: "What is Pinecone?"
Agent: Based on the knowledge base, Pinecone is a vector database built for machine learning applications that require fast, accurate vector search...
Sources:
- Document 2 (ID: doc2, Score: 0.9876, Category: databases): Pinecone Knowledge Base
- Document 3 (ID: doc3, Score: 0.8543, Category: databases): Pinecone Knowledge Base
Tool-Based Retrieval
The second agent only searches when it determines it's necessary:
User: "Tell me about RAG"
Agent: Let me search for relevant information about RAG.
[Searches knowledge base]
According to the search results, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines information retrieval with language generation for better AI responses...
Sources:
- Document 4 (ID: doc4, Score: 0.9234, Category: techniques): Pinecone Knowledge Base
Accessing Sources in Your Code
You can access the sources that were used in the retrieval from the response:
// After generating a response
const response = await agent.generateText("What is Pinecone?");
console.log("Answer:", response.text);
// Check what sources were used
const references = response.context?.get("references");
if (references) {
console.log("Used sources:", references);
references.forEach((ref) => {
console.log(`- ${ref.title} (ID: ${ref.id}, Score: ${ref.score}, Category: ${ref.category})`);
});
}
Customization Options
Different Embedding Models
You can use different OpenAI embedding models:
// More powerful but more expensive
const embeddingResponse = await openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-3-large", // 3072 dimensions
input: query,
});
// Balanced option (recommended)
const embeddingResponse = await openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-3-small", // 1536 dimensions
input: query,
});
// Legacy model
const embeddingResponse = await openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-ada-002", // 1536 dimensions
input: query,
});
Adding Your Own Documents
To add documents programmatically:
async function addDocument(content: string, metadata: Record<string, any> = {}) {
const index = pc.index(indexName);
// Generate embedding
const embeddingResponse = await openai.embeddings.create({
model: "text-embedding-3-small",
input: content,
});
const id = `doc_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`;
await index.upsert([
{
id,
values: embeddingResponse.data[0].embedding,
metadata: {
text: content,
...metadata,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
},
},
]);
return id;
}
Metadata Filtering
Pinecone supports advanced metadata filtering:
const searchResults = await index.query({
vector: queryVector,
topK: 10,
filter: {
category: { $eq: "documentation" },
timestamp: { $gte: "2024-01-01" },
},
includeMetadata: true,
});
Namespace Organization
Organize your data using namespaces:
// Use different namespaces for different data types
const index = pc.index(indexName).namespace("documentation");
const userIndex = pc.index(indexName).namespace("user-data");
await index.upsert([
{
id: "doc1",
values: embedding,
metadata: { type: "guide" },
},
]);
Best Practices
Index Design:
- Choose the right region for your users (lower latency)
- Use serverless for variable workloads
- Use pods for consistent high performance
- Consider costs vs. performance trade-offs
Embedding Strategy:
- Use
text-embedding-3-smallfor cost efficiency - Use
text-embedding-3-largefor maximum quality - Keep embedding model consistent across all documents
- Batch embedding generation to reduce API calls
Document Management:
- Include relevant metadata for filtering
- Use meaningful document IDs
- Consider document chunking for large texts
- Use namespaces to organize different data types
Performance:
- Limit search results (3-5 documents typically sufficient)
- Use metadata filtering to narrow searches
- Consider caching for frequently accessed documents
- Monitor query latency and costs
Security:
- Rotate API keys regularly
- Use environment variables for credentials
- Implement proper access controls
- Monitor usage for anomalies
Troubleshooting
Authentication Issues:
# Check if your API key is valid
curl -H "Api-Key: YOUR_API_KEY" https://api.pinecone.io/indexes
Index Creation Problems:
- Verify your Pinecone plan supports the index type
- Check if the index name already exists
- Ensure proper region availability
- Verify dimension matches your embedding model
Embedding Errors:
- Verify your OpenAI API key is valid
- Check API quota and billing
- Ensure network connectivity to OpenAI
- Monitor rate limits
No Search Results:
- Verify documents were upserted successfully
- Check embedding model consistency
- Try broader search queries
- Verify metadata filters aren't too restrictive
Performance Issues:
- Check index statistics for proper scaling
- Monitor query latency in Pinecone console
- Consider upgrading to pod-based indexes
- Optimize metadata filtering
This integration provides a production-ready foundation for adding semantic search capabilities to your VoltAgent applications. The combination of VoltAgent's flexible architecture and Pinecone's scalable vector search creates a robust RAG system that can handle enterprise-scale knowledge retrieval needs.